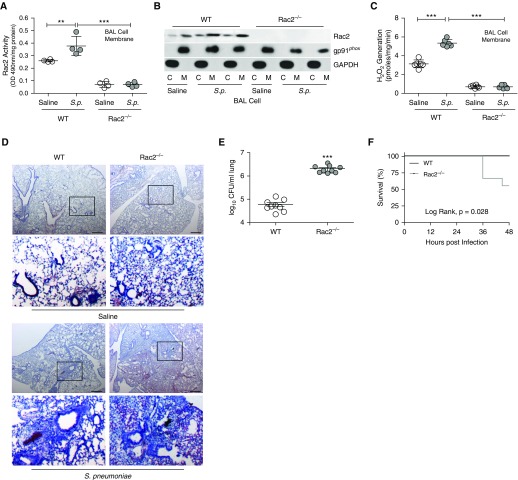
Figure 3.
Rac2−/− mice have impaired host defense. Wild-type and Rac2−/− mice were infected with Streptococcus pneumoniae. (A) Rac2 activity in BAL cell membrane (n = 4–5), (B) immunoblot analysis in cytosol and membrane fractions of BAL cells, and (C) NOX2 (NADPH oxidase 2)-derived reactive oxygen species generation in BAL cell membrane (n = 5). (D) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of lung tissues was performed (n = 4–5); and (E) lung colony-forming units (n = 9) and (F) Kaplan-Meier survival curves (n = 8–9) were determined. Scale bars, 600 μm. The second and fourth rows in D show magnifications of the boxed regions in the first and third rows, respectively. **P < 0.001; ***P < 0.0001. Values shown represent means ± SEM. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test was used for A and C; two-tailed Student’s t-test statistical analysis was used for E, and a log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test was used for F. Results from A–F were repeated three times with representative immunoblot and histology micrographs shown. C = cytosol; M = membrane; Rac2 = Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 2; S.p. = Streptococcus pneumoniae; WT = wild type.