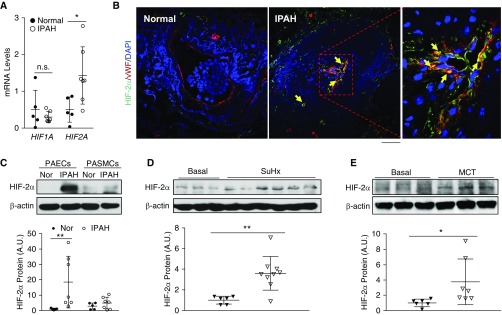
Figure 1.
Activation of HIF-2α (hypoxia-inducible factor-2α) signaling in lungs from patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH) and rodent PAH models. (A) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis showing increase in HIF2A but not HIF1A expression in the whole lungs of patients with IPAH compared with healthy donors. (B) Immunofluorescence staining against HIF-2α demonstrating upregulation of HIF-2α expression predominantly in endothelial cells (ECs) (vWF+). Arrows indicate HIF-2α (green)–positive ECs (red). Five normal donors and five patients with IPAH lung samples were analyzed. (C) Western blotting analysis demonstrating upregulation of HIF-2α in pulmonary arterial ECs (PAECs) but not pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells (PASMCs) isolated from patients with IPAH compared with healthy donors. (D) Upregulation of HIF-2α protein levels in lungs from Sugen 5416/hypoxia (SuHx) rats compared with age- and sex-matched controls. Lung tissues from SuHx rats were collected 6 weeks after the 3-week SuHx challenge. (E) Increase in HIF-2α protein levels in lungs of monocrotaline (MCT)-exposed rats compared with controls. Lung tissues from MCT rats were collected 4 weeks after MCT exposure. Bars represent mean values. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01. (A and C–E) Mann-Whitney test. (B) Scale bar: 50 μm. A.U. = arbitrary units; Nor = normal healthy donors; n.s. = not significant; vWF = von Willebrand factor.