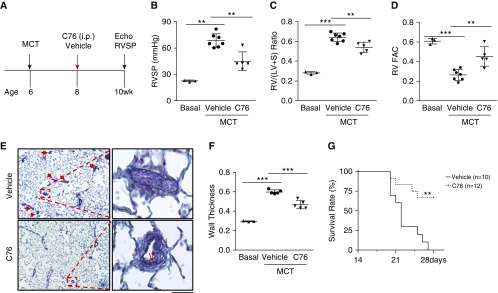
Figure 7.
HIF-2α (hypoxia-inducible factor-2α) inhibition halts pulmonary arterial hypertension progression and promotes survival of monocrotaline (MCT) rats. (A) Diagram showing the experimental timeline for C76 (compound 76) treatment in MCT rats. (B–D) C76 treatment reduced right ventricular systolic pressure (B) and right ventricular (RV) hypertrophy (C) and normalized RV contractility (D). (E) Representative micrographs of Russell-Movat pentachrome staining of MCT rat lungs. Arrows indicate vascular lesions. (F) Quantification of pulmonary arterial wall thickness in MCT rat lungs. (G) Marked increase in survival of C76-treated MCT rats compared with vehicle controls. The rats were challenged with MCT at (B–F) 32 mg/kg or (G) 35 mg/kg. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (B–D and F) One-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc analysis for multiple group comparisons; and (G) log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. (E) Scale bar: 50 μm. RV FAC = right ventricular fractional area change; RV/(LV + S) = ratio of right ventricle to left ventricle plus interventricular septum; RVSP = right ventricular systolic pressure; V = vessel.