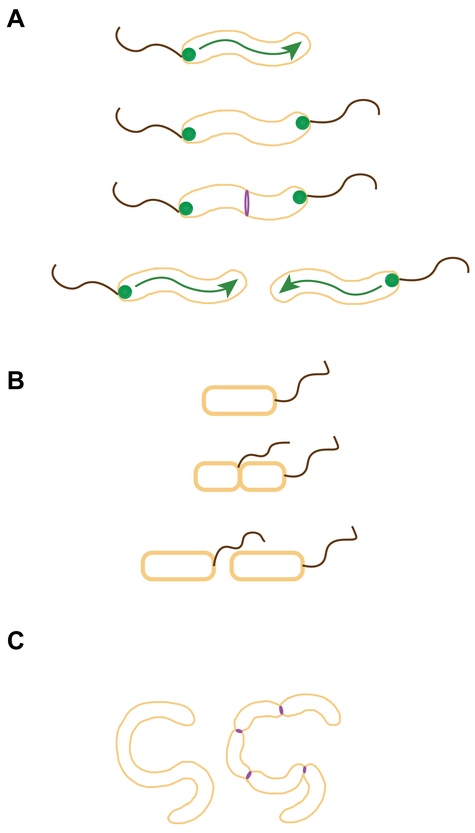
Figure 3.
Cell division regulation in polar flagellates. (A) In C. jejuni, FlhG (green circles), a MinD/ParA-like ATPase that regulates flagellar copy number, also participates in negatively regulates FtsZ (purple) assembly near poles. (B) In a magnetotactic Gammaproteobacterium, flagella arise from the site of cell division (suggesting positive cell division regulation), perhaps to ensure that the flagella of daughter cells are oriented in the same direction as the parental cells along earth’s the magnetic dipole. (C) Cells of B. bacteriovorus grow as filaments inside the periplasm of Gram-negative bacteria. Just prior to host cell lysis, the filamentous cell undergoes synchronous septation (reminiscent of sporulating S. coelicolor cells) to liberate motile daughter cells. Possible sites of FtsZ ring assembly (purple) are shown; flagella arising from the site of septation are not depicted.