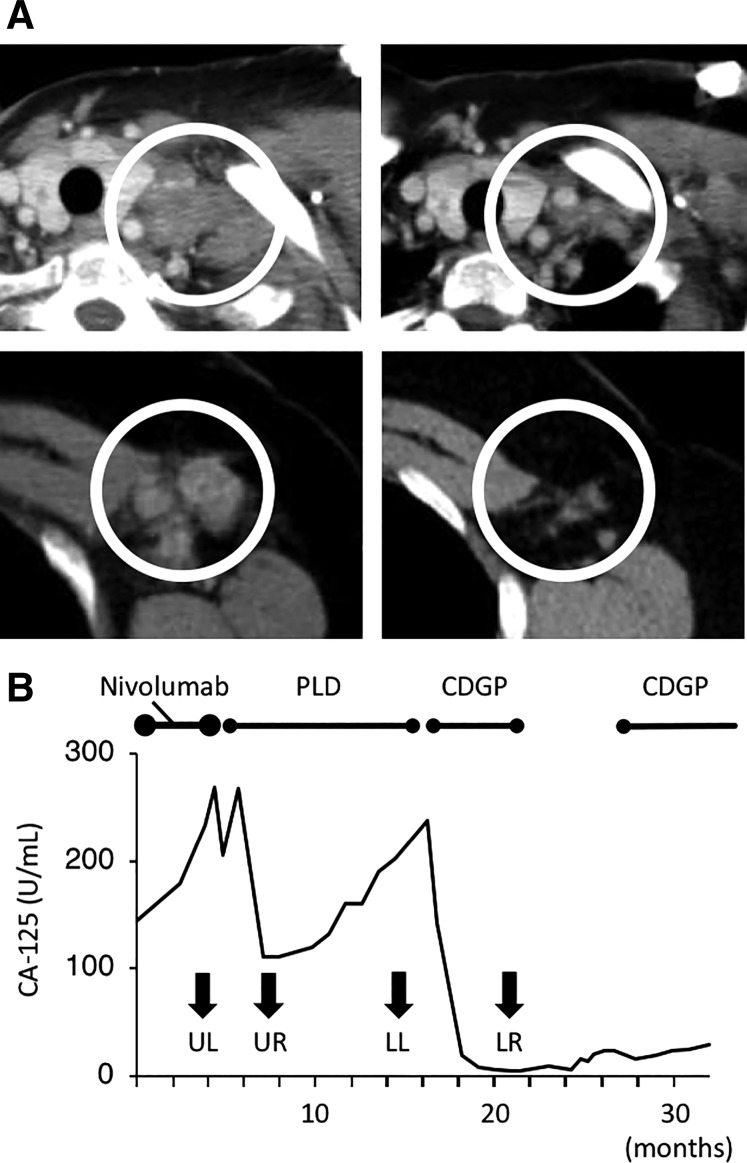
Figure 1.
Antitumor effect of palliative chemotherapy after the nivolumab trial in Case 1 (Patient 13). (A): Computed tomography images. (Upper left): A left subclavicular lymph node before PLD therapy. (Upper right): The same lymph node after three cycles of PLD. (Lower left): A left axillary lymph node before CDGP therapy. (Lower right): The same node after six cycles of CDGP. PLD was used after the patient developed progressive disease (PD) with nivolumab. With PLD treatment, the short axis of the lymph node decreased from 22.5 mm to 7.9 mm (−65%). CDGP was administered after the patient developed PD after 12 cycles of PLD. The short axis of the lymph node decreased from 14.9 mm to 6.9 mm (−54%). The white circles in each image indicate enlarged lymph nodes. (B): Serum CA‐125 levels. Serum CA‐125 levels decreased after PLD and CDGP. Both agents resulted in a partial response. Arrows indicate CA‐125 levels at the time when images in (A) were obtained. CDGP was administered again as palliative chemotherapy after a 6‐month chemotherapy‐free period because it had been quite effective.
Abbreviations: CA‐125, carbohydrate antigen 125; CDGP, nedaplatin; LL, Figure 1A lower left; LR, Figure 1A lower right; PLD, pegylated liposomal doxorubicin; UL, Figure 1A upper left; UR, Figure 1A upper right.