Fig. 1.
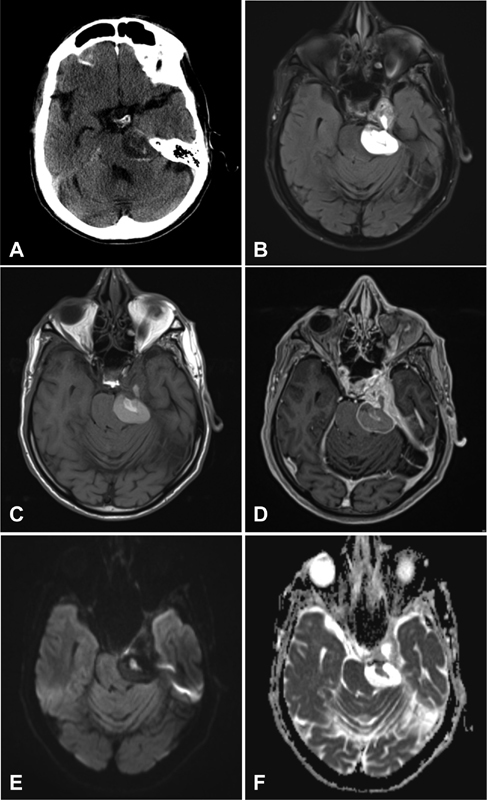
Preoperative axial ( A ) computed tomography (CT) of the head shows a complex mass within the left cavernous sinus and CPA cistern compressing the left pons. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) ( C – E ) reveals a solid and cystic mass centered at the cavernous sinus and Meckel's cave with a bulky hemorrhagic extension to the CPA cistern. The main mass is isointense on T1-weighted images ( C ) and heterogeneously isointense on T2-weighted images ( B ) with multilocular small cysts containing hemorrhagic layering. The solid component of the lesion is avidly enhancing on postcontrast images ( D ). Signal of diffusion-weighted sequence imaging is lower than the brain parenchyma ( E ) with ADC value of 1,300 ± 643 (× 10 −6 mm 2 /s; F ). CPA, cerebellopontine angle. ADC, apparent diffusion coefficient.
