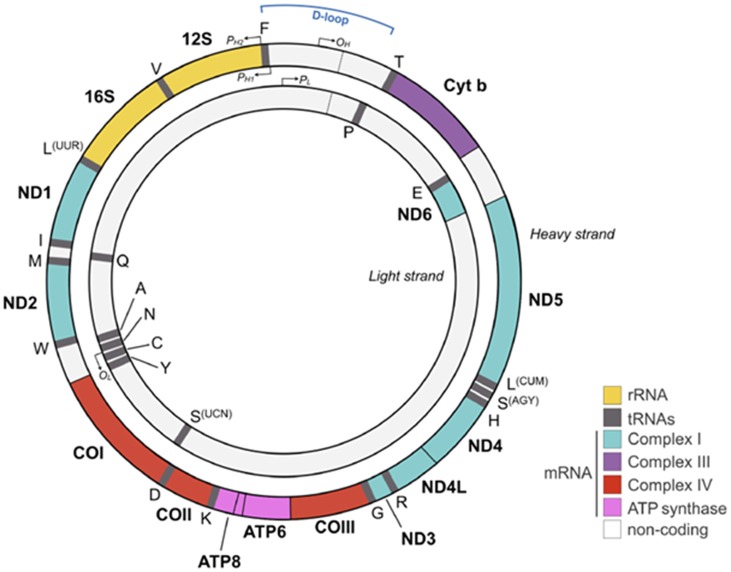
Figure 1.
Human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). The mtDNA consists of a light (inner) and heavy (outer) circular DNA strand with each containing a separate origin of replication termed OL and OH, respectively. The mtDNA comprises 16,569 nucleotides and encodes 37 genes, including 2 ribosomal and 22 transport RNAs required for protein synthesis. Mitochondrial encoded proteins constitute essential parts of the respiratory chain by contributing seven subunits to complex I, one subunit to complex III, three subunits to complex IV, and two subunits to complex V (adenosine triphosphate, ATP synthase). Promoters on the heavy strand (PH1 and PH2) and on the light strand (PL) drive mtDNA gene expression. The glucocorticoid receptor (GR) binds to the mtDNA near the D-loop straddling the OH origin. Colors for each gene match the respiratory chain complexes shown in Figures 2, 5. 1 is adapted from Picard and McEwen (2018) license number 4360110364852.