Figure 5.
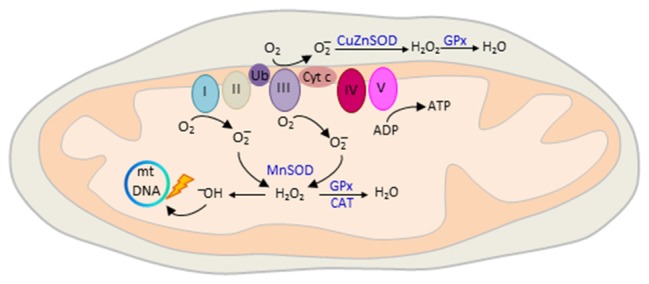
Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. The mitochondrial electron transport chain (ETC) consists of five interacting protein complexes numbered I to V that build a proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane. Electron leakage mainly at complex I and III reduces prematurely oxygen to superoxide anion () during erobic respiration. is converted by mitochondrial superoxide dismutase MnSOD and CuZnSOD to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in the matrix or intermembrane space, respectively. Thereafter, H2O2 is oxidized to highly reactive hydroxyl (OH−) free radicals that cause mtDNA damage, reduced transcription and oxidation of ETC proteins and membrane lipids. ROS production is counteracted by enzymatic defense mechanisms including glutathione peroxidase (GPx) and catalase (CAT) that detoxify H2O2 into water. Colors from respiratory complexes match the contribution of mitochondrial gene products shown in Figure 1. Ub, ubiquinone, also known as Coenzyme Q10; Cyt c, cytochrome c.
