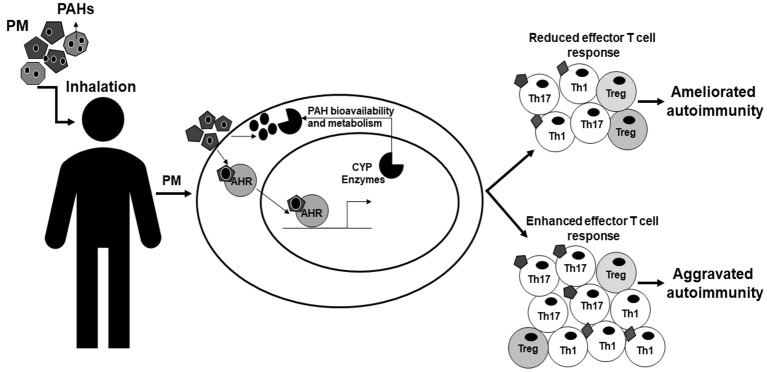
Figure 3.
Model of AHR modulation of PM-mediated autoimmunity. This figure is adapted from O'Driscoll et al. (100) and demonstrates how AHR may modulate PM-mediated autoimmunity. PM is inhaled by people and once inhaled is able to be taken-up and has the capacity to activate the AHR in cells within the body. AHR ligands, such as PAHs, adhered to atmospheric PM activate the AHR and cause the AHR to translocate to the nucleus and bind DNA elements such as XRE, inducing genes including CYP enzymes. The extent and duration of activation of AHR ligands shifts the immune balance enhancing effector T cells worsening autoimmunity or suppressing T cell responses and ameliorating autoimmunity. The AHR ligands adhered to the particulate have the potential to become bioavailable through metabolism or other mechanisms and then can be metabolized by CYP enzymes potentially causing other immune related effects or altering the immune responses. AHR, aryl hydrocarbon receptor; PM, particulate matter; PAHs, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons; XRE, xenobiotic response element; CYP, cytochrome P450. This figure or a version of this figure was published in Particle and Fibre and Toxicology and is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International Public License.