Figure 1.
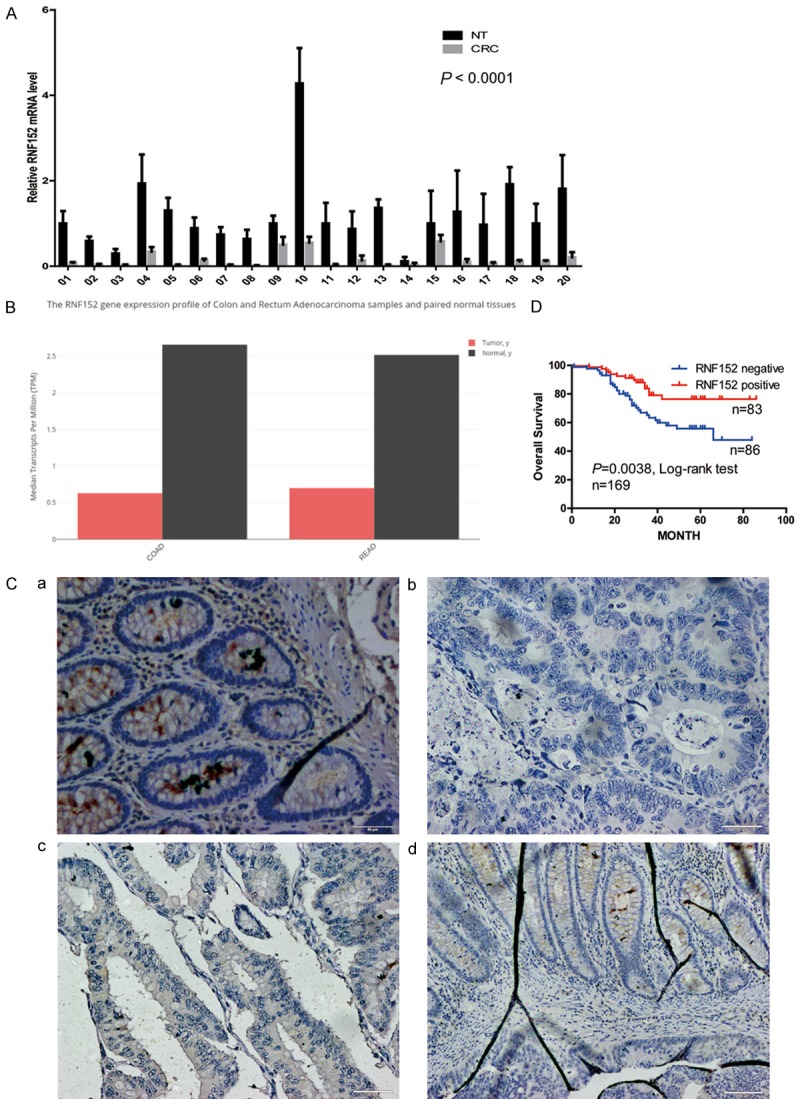
Reduced expression of RNF152 in CRC. (A) QPCR detection of RNF152 expression in 20 CRC tumor tissue samples and corresponding normal mucosa. RNF152 mRNA expression was significantly declined in CRC tissue compared with normal tissue. Student’s paired t-test; P<0.0001. (B) Expression of RNF152 in Colon Cancer and Rectal Cancer in TCGA Database (http://gepia.cancer-pku.cn). RNF152 mRNA expression was significantly declined in CRC tissue compared with normal tissue. The y-axis stands for the median RNF152 transcripts per million (TPM). (C) Immunohistochemical analysis of RNF152 in CRC and normal mucosa tissue samples. Representative images of (a) positive RNF152 expression of normal mucosa tissue, (b) negative expression of RNF152 in CRC cells, (c) positive expression of RNF152 in CRC cells, and (d) RNF152 expression in CRC cells in the invasive margin. In the invasive margin of CRC tissue, CRC cells did not express RNF152. But the normal colonic gland, which has not been invaded by CRC cells, expressed high level of RNF152. (Ca-Cc) Magnification, 200 ×. Scale bar, 50 μm; (Cd) Magnification, 100 ×. Scale bar, 100 μm. (D) RNF152 expression-stratified Kaplan-Meier plots for overall survival in CRC patients, negative RNF152 expression was significantly associated with shortened patient survival. Statistical significance was determined by a log-rank test. P = 0.0038, n = 169. RNF152: Ring Finger Proteins 152; CRC: colorectal cancer; TCGA: The Cancer Genome Atlas; QPCR: quantitative-polymerase chain reaction.
