Figure 7.
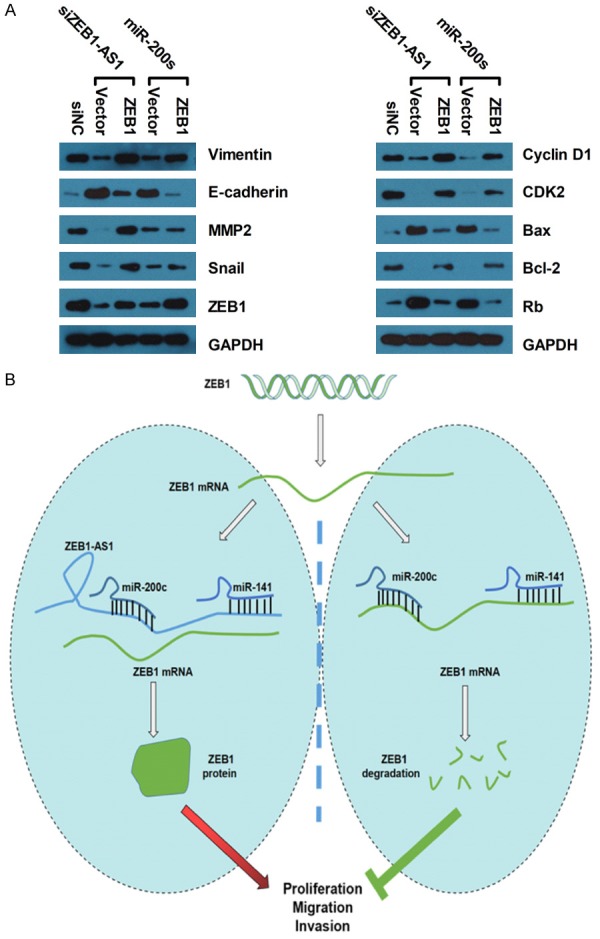
Possible signaling pathways of ZEBA-AS1/miR-200c/141-ZEB1 involved in glioma cancer progression. (A) Representative western blot results of EMT (E-cadherin, Vimentin, MMP2, Snail and ZEB1), cell cycle (Cyclin D1, Rb and CDK2) and apoptosis (Bax and Bcl-2) markers. GAPDH was used as the normal control. The original whole film of western blotting in (A) was presented in Supplementary Figure 1. (B) A diagram exhibiting the role and regulatory mechanisms of the ZEB1-AS1/miR-200c/141-ZEB1 axis in glioma cancer. In the ZEB1-AS1 depletion cells, upregulated miR-200c/141 inhibits glioma cancer cell proliferation, cell cycle, motility, and apoptosis-resistance by targeting ZEB1. On the contrary, ZEB1-AS1 overexpression suppresses miR-200c/141 expression, which then activates ZEB1 and promotes glioma cancer cell proliferation, cell cycle, motility, and apoptosis-resistance.
