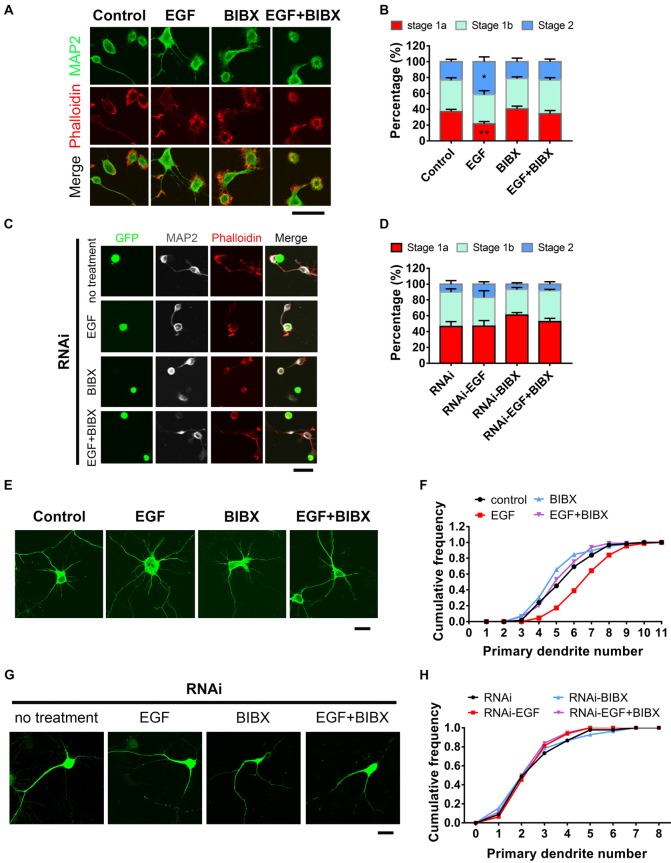
Figure 3.
HIP1R is necessary for epidermal growth factor (EGF) induced-acceleration of neurite initiation and dendrite arbor growth. (A) Representative images of DIV 0 neurons treated with EGF (50 ng/ml), BIBX (0.5 μM) or EGF+BIBX and labeled for MAP2 (green), pallolidin (red), harvested 4–5 h after plating. Scale bar, 20 μm. (B) Quantification of neurite initiation after EGF treatment (n = 4,100 neurons for Control, 4,372 neurons for EGF, 5,003 neurons for BIBX and 3,913 neurons for EGF+BIBX treated neurons; ≥3 independent cultures; unpaired two-tailed t-test). (C,D) Representative images (C) and neurite initiation stage quantification (D) of HIP1R-RNAi neurons EGF, BIBX or EGF+BIBX, harvested 5–6 h after plating (n = 1,419 neurons for RNAi, 1,040 neurons for EGF, 1,642 neurons for BIBX and 1,368 neurons for EGF+ BIBX treated neurons; three independent cultures; unpaired two-tailed t-test). Scale bar, 20 μm. (E) Representative images of DIV 6 neurons treated with EGF, BIBX or EGF+BIBX. Scale bar, 20 μm. (F) Cumulative distribution of primary dendritic numbers of control, EGF, BIBX or EGF+BIBX treated groups (n = 62, 87, 85 and 94, respectively; three independent cultures). (G) Representative images of HIP1R-RNAi neurons without treatment and treated with EGF, BIBX or EGF+BIBX at DIV 6. Scale bar, 20 μm. (H) Cumulative distribution of primary dendritic numbers of HIP1R-RNAi neurons with or without treatment (n = 64, 64, 83 and 80, respectively; three independent cultures). All data are presented as mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.