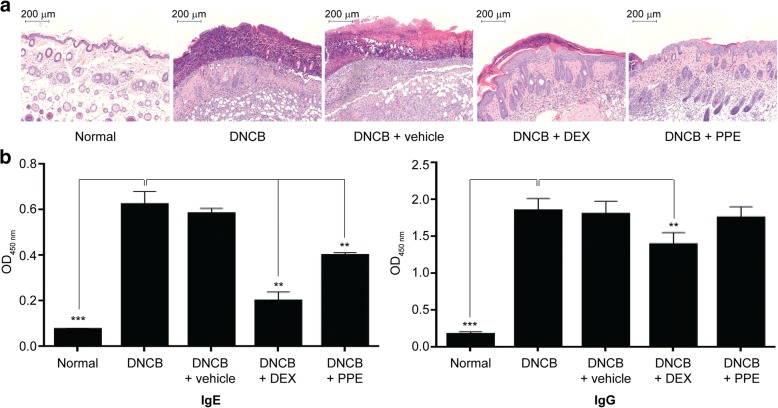
Fig. 3.
Inhibitory effect of PPE on DNCB-induced inflammation based on histological analyses and serum IgE levels. (a) Histopathological changes in mouse dorsal inflammatory lesions were analyzed via H&E staining. Abnormal thickening of the epidermis along with severe keratinization and massive infiltration of immune cells were observed in DNCB-treated mice. Co-treatment with PPE significantly suppressed epidermal hyperplasia whereas cream alone had no effect. DEX treatment was used as a positive control. (b) IgE and IgG levels. Serum IgE and IgG contents were measured using ELISA kits. Both IgE and IgG levels were significantly enhanced (up to 9-fold) following DNCB treatment. Only allergen-specific IgE levels were significantly reduced after PPE treatment whereas IgG levels were maintained. Cream (vehicle) alone had no suppressive effect on either IgE or IgG levels. Results are presented as means ± SD of independent biological replicates (n = 3). The two-tailed student t-test was used to evaluate the statistical significance of differences between DNCB-treated and normal, PPE or DEX-treated groups (** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001)