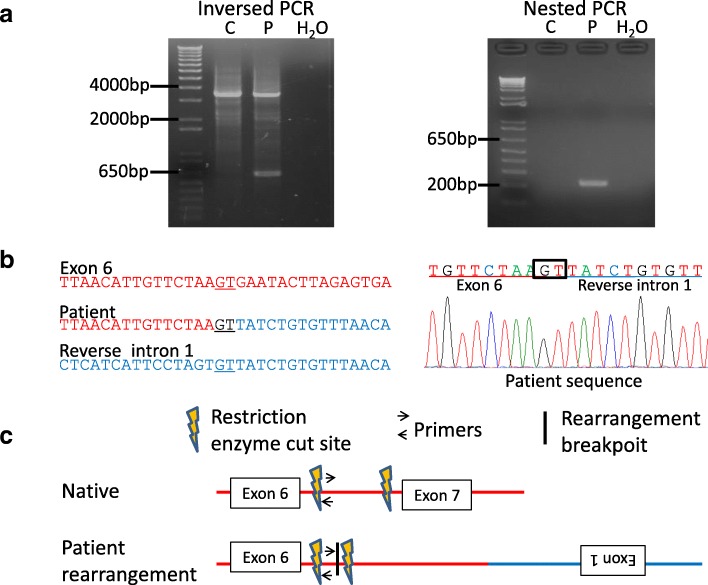
Fig. 2.
Identification of the duplication junction via inverse PCR. a Isolation of the junction fragment. Two distinct inverse PCR products were observed following agarose gel electrophoresis. The larger product was derived from a normal allele and the small product from a rearranged allele (left). The amplified products were purified following nested PCR (right). P, patient; C, control; H, H2O. b Sanger sequencing of the PCR products including the junction. The unknown sequence next to the junction was identified as intron 1 of the OTC gene in the reverse orientation. The normal exon 6 and intron 1 sequences are aligned in red and blue typeface, respectively. Underlined nucleotides indicate microhomology at the breakpoint junction. c Predicted structure of the junction. Horizontal arrows indicate the recognition sites of the primers used for inverse PCR and the vertical arrows denote the TaqI restriction sites