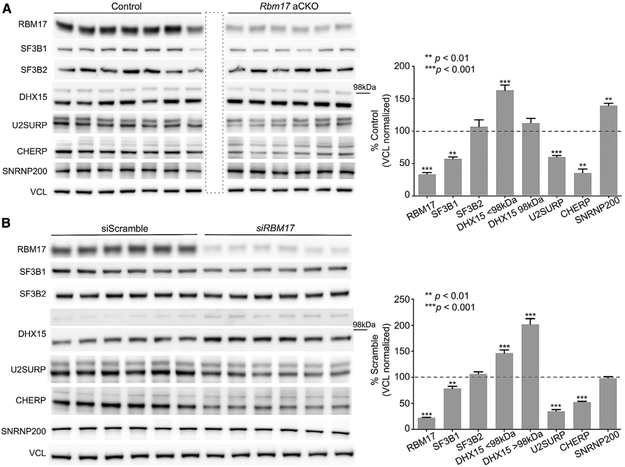
Figure 2. Rbm17 Deletion in Adult Mice Is Lethal, and Knockdown Alters Levels of Its Interactors.
(A) Representative western blots (left) and protein-level quantifications (right) of the six validated interactors of RBM17 in Rbm17 adult conditional knockout (aCKO) mice versus control littermates (n = 6 aCKO and n = 7 control littermates). The area boxed by a dashed line indicates an empty well.
(B) Representative western blots (left) and protein-level quantifications (right) of the six validated interactors of RBM17 in HEK293T treated with siRBM17 or siScramble (n = 6–18 replicates/siRNA). All data were normalized to mouse or human Vinculin (VCL), used here as loading control.
For both panels, bars represent mean ± SEM; p value was calculated by two-tailed Student’s t test, and significance was set at p < 0.05. The 98 kDa mark indicates the relative position of the two bands detected for DHX15 and does not concern any of the other proteins. See also Figure S2.