Figure 4.
Accuracy of species delimitation using the gdi with parameters estimated from data of 50 loci using (a) phrapl and (b) bpp. Species status is defined using the gdi at different cutoffs (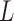 and
and 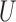 ). This is calculated by simulating 10,000 gene trees under the MSC model with migration for phrapl, and analytically for bpp. Along the
). This is calculated by simulating 10,000 gene trees under the MSC model with migration for phrapl, and analytically for bpp. Along the 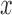 -axis, each group of bars gives results for different gdi cut-offs. Below the lower bound (
-axis, each group of bars gives results for different gdi cut-offs. Below the lower bound (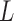 ), populations
), populations 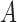 and
and 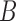 are defined as a single species; above the upper bound (
are defined as a single species; above the upper bound ( ),
), 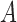 and
and 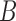 are defined as separate species, while between the bounds, the species status is ambiguous. The six bars within each group represent the six sets of species divergence times (
are defined as separate species, while between the bounds, the species status is ambiguous. The six bars within each group represent the six sets of species divergence times (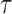 s). The bar shadings are white = the inferred delimitation outcome matched the true outcome; light green/gray = ambiguity was inferred when the true delimitation is known (insufficient power); dark green/gray = delimitation was inferred (whether one or two species) when the truth was ambiguous (excessive confidence); and black = one species was inferred when there were two, or vice versa. The results for phrapl are recreated using the R code from Jackson et al. (2017, Fig. 4).
s). The bar shadings are white = the inferred delimitation outcome matched the true outcome; light green/gray = ambiguity was inferred when the true delimitation is known (insufficient power); dark green/gray = delimitation was inferred (whether one or two species) when the truth was ambiguous (excessive confidence); and black = one species was inferred when there were two, or vice versa. The results for phrapl are recreated using the R code from Jackson et al. (2017, Fig. 4).

