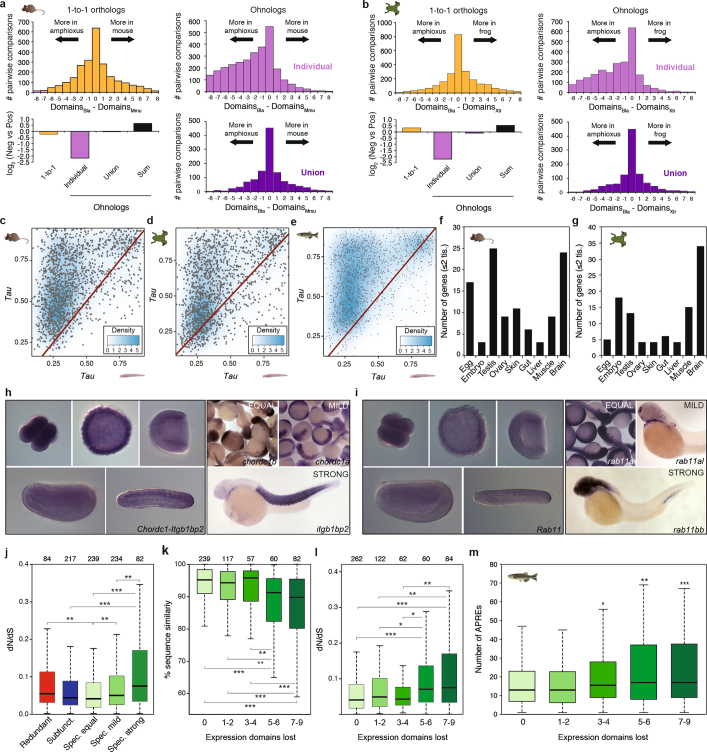
Extended Data Fig. 10. Regulatory evolution after vertebrate WGD.
a, b, For each mouse (a) or frog (b) gene, the number of positive-expression domains across nine equivalent samples is subtracted from the number of domains in which the single amphioxus orthologue is expressed. The distribution of the difference in domains between the amphioxus and the vertebrate species is plotted for 1-to-1 orthologues (2,450 and 2,484 gene pairs for mouse and frog, respectively; yellow), individual ohnologues (3,011 and 2,637 gene pairs in 1,212 and 1,094 families for mouse and frog, respectively; lilac) and the union of all vertebrate ohnologues in a family (purple). Bottom left, log2 of the ratio between the sum of all mouse (a) or frog (b) genes with negative versus positive score for each orthology group. ‘Sum’ (black), binarization of family expression is performed after summing the raw expression values for all ohnologues. c–e, Density scattered plot of the τ values for pairs of mouse (c, n = 1,502), frog (d, n = 1,495) and zebrafish (e, n = 1,498) and amphioxus orthologues from multi-gene families in vertebrates. f, g, Number of ohnologues with strong specialization (≤2 remaining expression domains) in mouse (f) or frog (g) expressed in each tissue or developmental stage. h, i, Representative in situ hybridization assays in zebrafish embryos for different members of specialized families (right) and for the single amphioxus orthologue (left) (Chordc1 and Itgb1bp2 (h) and Rab11 (i)). Zebrafish image data for this paper were retrieved from the Zebrafish Information Network (ZFIN), University of Oregon, Eugene, OR 97403-5274; (http://zfin.org/, accessed May 2018) and are used with the permission of B. Thisse. Amphioxus in situ hybridization was performed once using 10 embryos per probe, all of which showed the same expression pattern. j, Distribution of the dN/dS ratio between human and mouse for different classes of ohnologues based on their fate after WGD. k, l, Distribution of the percentage of nucleotide sequence similarity (k) or dN/dS ratio (l) between human and mouse for ohnologues grouped by the number of expression domains lost. m, Distribution of the number of APREs within GREAT regions for zebrafish ohnologues grouped by the number of expression domains lost. P values in j–m correspond to Wilcoxon sum-rank tests. *0.5 > P value ≥ 0.01; **0.01 > P value ≥ 0.001; ***P value < 0.001.