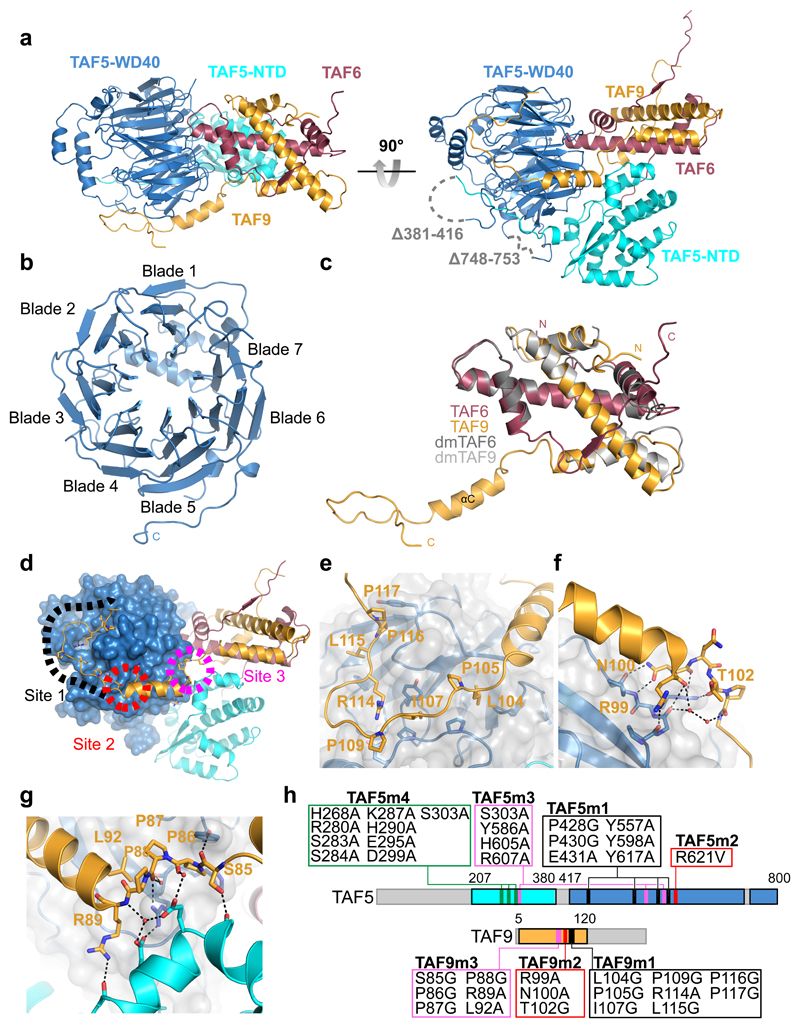
Figure 2. Crystal structure of TAF5-TAF6-TAF9 complex.
a, The TAF5-TAF6-TAF9 complex is shown in a cartoon representation in two views. The TAF6-TAF9 HFD heterodimer is intimately wedged in between the TAF5 NTD and WD40 repeat domain. TAF5 NTD and WD40 repeat domain are colored in cyan and blue, respectively. TAF6 is colored in red, TAF9 is colored in orange. Disordered loops are drawn as grey dashed lines. b, The TAF5 WD40 repeat domain is viewed from its bottom cavity, adopting a 7-bladed β-propeller. c, Human TAF6-TAF9 superimposed on the TAF6-TAF9 HFD dimer from D. melanogaster (PDBID 1TAF 29). D. melanogaster proteins are colored in grey, human TAF in red and human TAF9 in orange. Note the extended C-terminal domain in human TAF9. d, Overview of the structure with the three major interactions anchoring TAF9 to TAF5.e-g, Zoom-in showing TAF9 C-terminal loop (e), hydrogen-bond network at C-terminus of helix αC (f), and triple proline-turn (g). h, Mutations to probe TAF5-TAF9 interfaces. Colors as in (d); green indicates mutated region in TAF5 NTD targeting TAF5-TAF6-TAF9 interface.