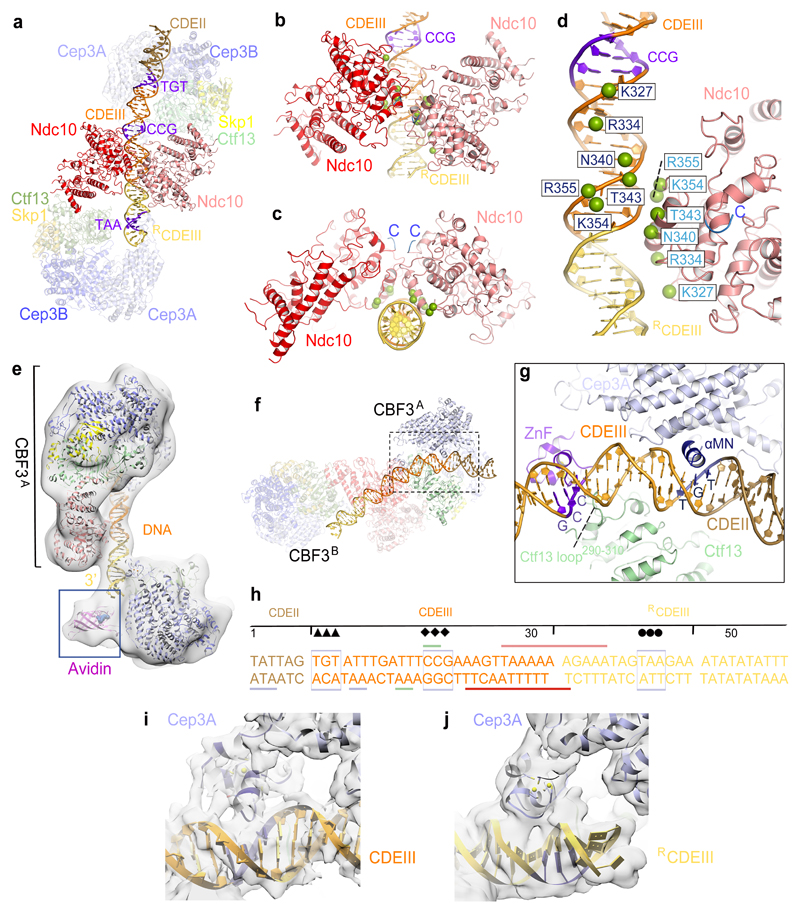
Figure 3. Basis for CBF3−CEN3 recognition.
(a) Overview of the dimeric CBF3−CEN3 complex. (b) and (c) Two views of the Ndc10DBD-DNA interface. DNA induces dimerization of Ndc10DBD. (d) Details of Ndc10DBD−DNA contacts. Residues in contact with DNA are shown as green spheres. Cartoon representation of only one Ndc10 subunit is shown. (e) EM density map of the CBF3−CEN3-biotin avidin complex orients and positions the DNA duplex. (f) Overview of Cep3B-Ctf13 contacts with DNA in CBF3A. (g) Details of Cep3A−Ctf13−CDEIII interface, showing Zn2Cys6 cluster contacting the CCG motif and αMN helix contacting the TGT motif. Ctf13 contacts the minor groove midway between the CCG and TGT motifs. (h) Schematic of CBF3-DNA interactions. Sequence of the nuclease resistant 56 bp segment protected by CBF3 is shown 17. Arrow, diamond and circle symbols as in Fig. 1i. Colored horizontal lines indicate contacts to CBF3 subunits. (i) and (j) EM density of the Zn2Cys6 clusters interacting with CEN3-DNA for (i) Cep3A of CBF3A and (j) Cep3A of CBF3B.