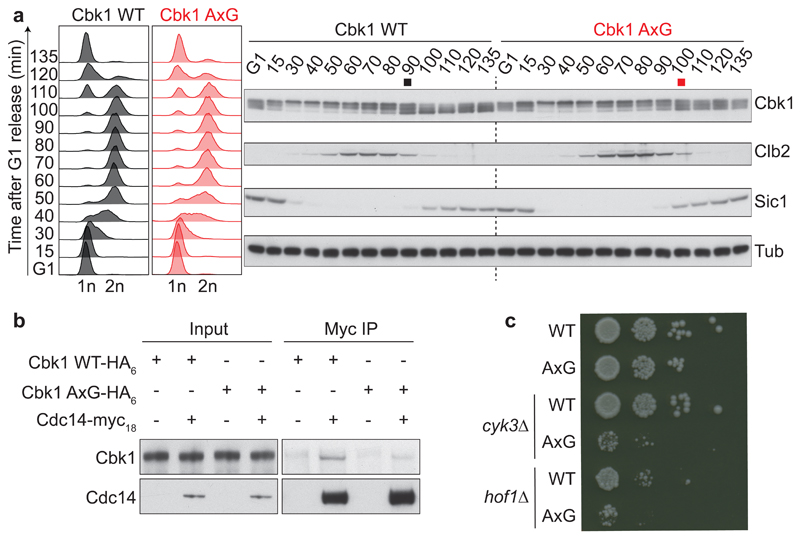
Fig. 2. The PxL motif promotes Cbk1 dephosphorylation.
a, Strains expressing wild type Cbk1 or Cbk1 AxG progressed synchronously through the cell cycle following α-factor arrest and release. FACS analysis of DNA content confirmed cell cycle synchrony. Western blotting was used to analyze the Cbk1 phosphorylation status, as well as Clb2 and Sic1 levels which served as additional cell cycle markers. The black and red squares mark the approximate midpoints of Cbk1 dephosphorylation. Tubulin served as a loading control. Uncropped images of all the blots are found in Supplementary Data Set 1. b, The Cdc14-Cbk1 interaction depends on the PxL motif. Cdc14-myc18 was immunoprecipitated from asynchronously growing control or Cbk1 AxG cells and Cbk1 co-purification analyzed by western blotting. c, Synthetic growth defect of Cbk1 AxG in the absence of cytokinesis factors. Ten-fold serial dilutions of the indicated strains were spotted onto YPD plates and grown at 25 °C for two days.