Figure 5. HPO-30 interacts with the WRC.
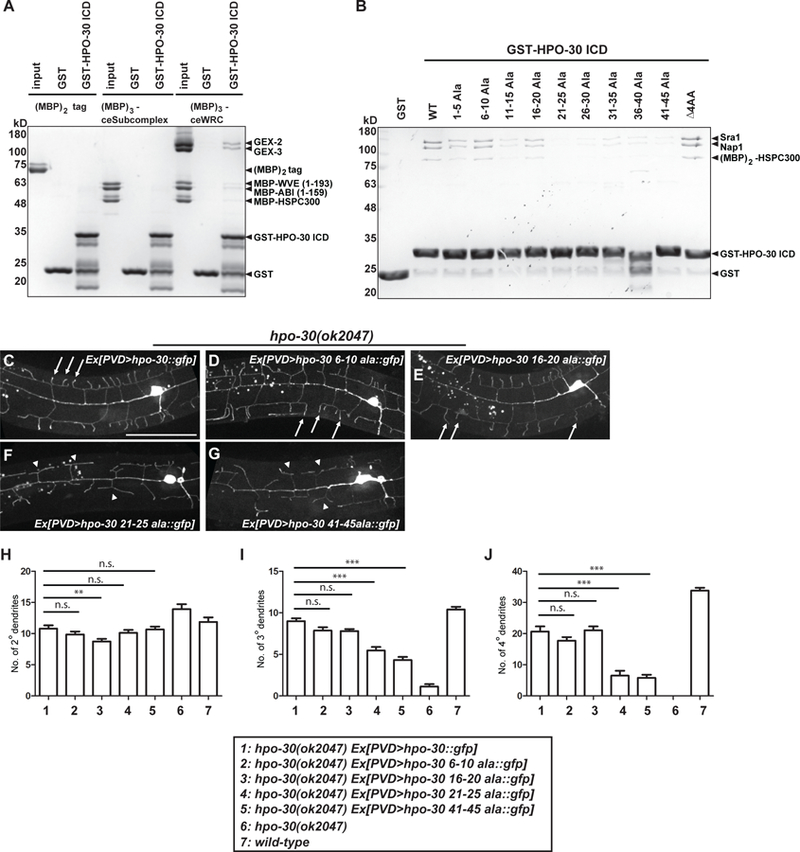
(A-B) Coomassie-blue-stained SDS-PAGE gel showing GST-HPO-30 ICD pull-down of C. elegans WRC (A) and human WRC (B). In (A), the input lanes were loaded with 3 pmol of the MBP-tagged proteins. In (B), GST-HPO-30 ICDs with indicated alanine scan mutations were compared. The numbers in the name of each construct indicate the position of the mutated amino acids in the cytosolic part of HPO-30 (the last 51 amino acids). △4AA means deletion of the last 4 amino acids of HPO-30. (C-G) Representative confocal images showing the morphologies of PVD dendritic arbors. PVD was labeled by GFP fused to the re-expressed wild-type or mutant forms of HPO-30 in hpo-30 null mutant animals. Arrows: 4o branches in fully rescued animals. Arrow heads: 2o branches that failed to form 4o branches. Scale bar = 50 μm. (H-J) Quantification of the number of 2o, 3o and 4o branches in a region 100 μm anterior to the PVD cell body. Data are represented as mean ± SEM, with 15 animals quantified for each genotype. One-sided ANOVA with Dunnett’s test was used for statistical analysis. **: p<0.001. ***: p< 0.0001. n.s.: not significant. See also Figure S3 and S6.
