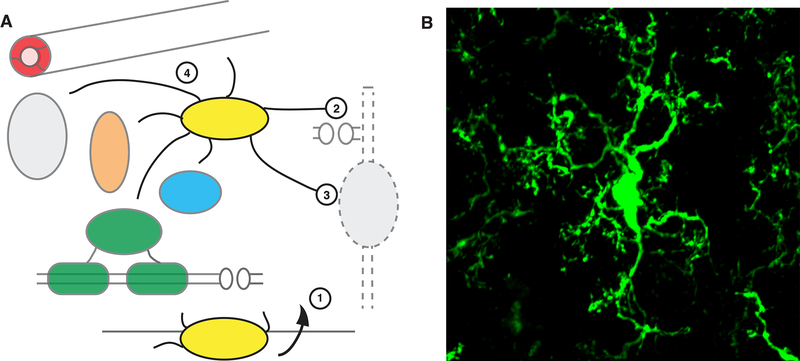
Figure 4. Microglia.
A: Microglia are the resident immune cells of the brain, entering during early development from the periphery (1). In addition to immune surveillance roles (not shown), microglia interact with multiple cell types of the CNS and regulate numerous developmental and functional processes, including synaptic pruning (2), clearing apoptotic neurons (3) and interacting with multiple CNS cell types, in health and disease (4). B: Microglia expressing GFP in mouse cortex (Cx3cr1-GFP), courtesy of Youtong Huang and Greg Lemke, Salk Institute.