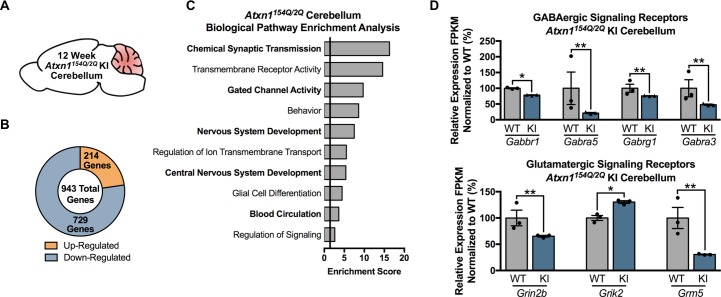
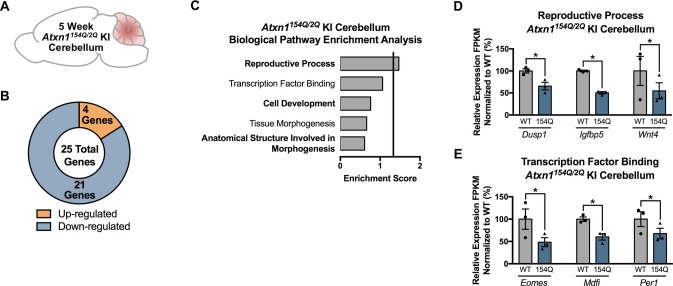
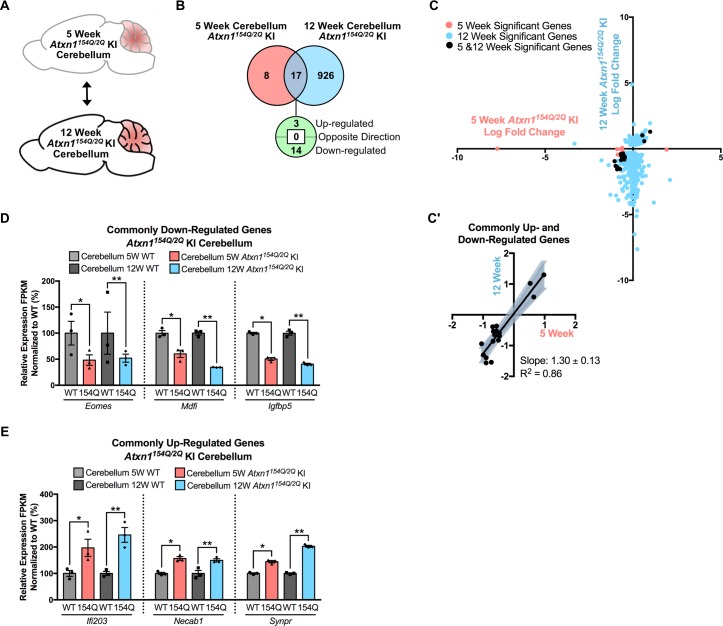
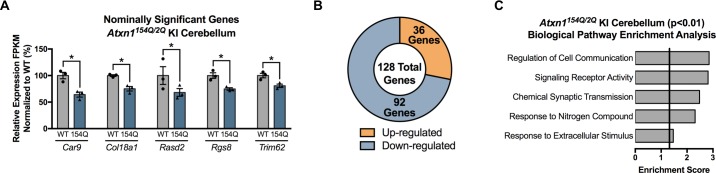
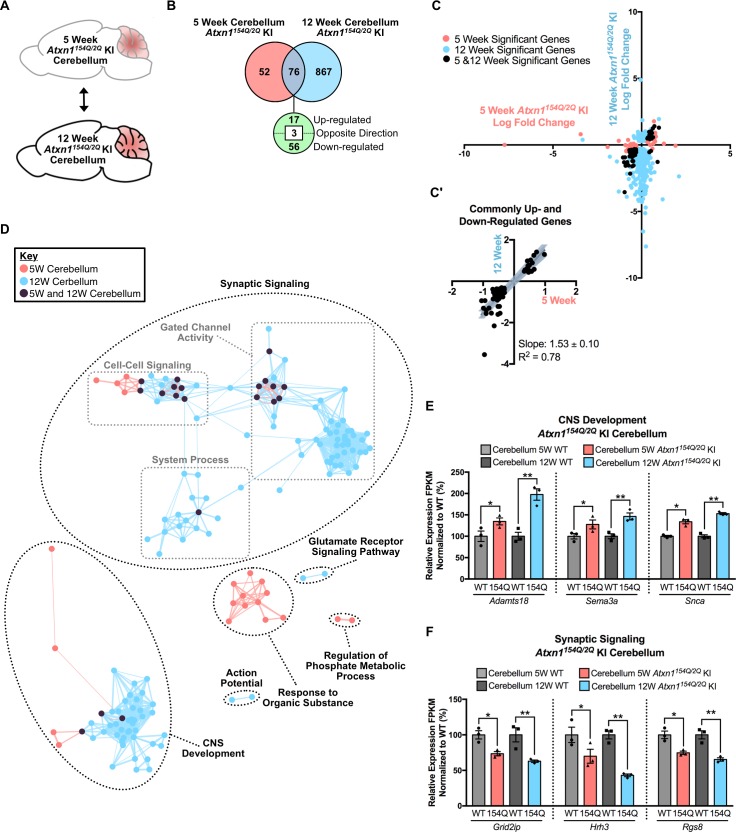
(A) Schematic of the time-point comparison in Atxn1154Q/2Q KI cerebellum. (B) Total number of differentially regulated genes in the Atxn1154Q/2Q KI cerebellum relative to appropriate WT controls that are common, and uniquely altered, in each time-point (nominal p-value < 0.01 for 5 week dataset; FDR p-value < 0.05 for 12 week dataset; n = 3 males per genotype for each time-point for RNA-seq). (C) Dot plot of log fold changes for genes altered in the 5 and 12 week Atxn1154Q/2Q KI cerebellum. Nominal p < 0.01 for the 5 week dataset, FDR p-value < 0.05 for the 12 week dataset. (C') Log fold change of genes up- or down-regulated in both the 5 week and 12 week time-points only. Dysregulated gene were excluded from this analysis. Linear regression analysis identified the slope and R2 of these log fold changes (slope = 1.53 ± 0.10; R2 = 0.78). A total of 73 genes were plotted in this analysis. (D) Clustering of GO terms identified from the Atxn1154Q/2Q KI cerebellum 5 week and 12 week differentially regulated gene lists relative to the appropriate WT controls. For this analysis, genes with a nominal p-value < 0.01 were used to generate the GO list for the 5 week Atxn1154Q/2Q KI cerebellum, and FDR p-value < 0.05 was used for the 12 week cerebellum. (E) A subset of genes associated with CNS Development were commonly up-regulated and (F) a subset of Synaptic Signaling genes were commonly down-regulated when assessed in the 5 and 12 week time-point. * nominal p-value < 0.01; ** FDR p-value < 0.01 (n = 3 males per genotype for each time-point).