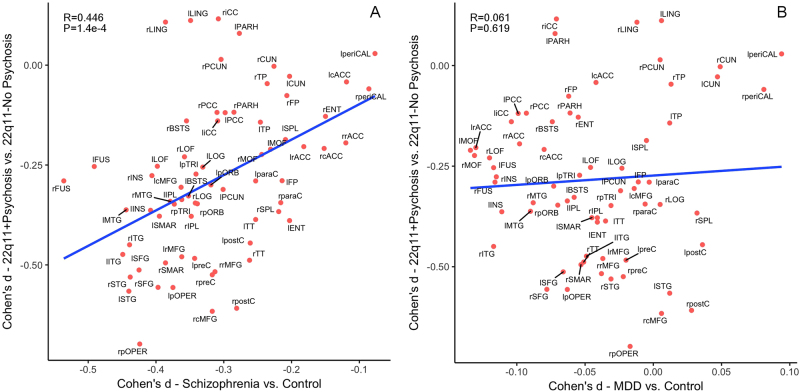
Fig. 3.
Pattern similarity in CT deficits between 22q11DS with psychosis and idiopathic schizophrenia, in contrast to major depressive disorder (MDD). Here we correlated the effect sizes (Cohen’s d) for regional CT measures from the comparison between 22q11DS + Psychosis and 22q11DS-No-Psychosis groups with those from the ENIGMA Schizophrenia working group [47], in contrast to the ENIGMA MDD study [35]. a Correlation in the effect sizes of CT deficits between idiopathic schizophrenia and 22q11 + Psychosis; b Correlation in the effect sizes of CT deficits between MDD and 22q11 + Psychosis. The effect sizes for CT deficits from psychotic vs. non-psychotic 22q11DS comparisons were significantly correlated with those in ENIGMA idiopathic schizophrenia vs. control comparisons. In contrast, the same effect sizes were not significantly correlated with those in ENIGMA MDD vs. control comparisons. Both x- and y-axes represent effect sizes in Cohen’s d in the above-mentioned comparison for all 68 cortical regions derived from the FreeSurfer cortical parcellation. Abbreviations of the cortical regions are adopted from the brainGraph package [67] as follows: BSTS banks of superior temporal sulcus, cACC caudal anterior cingulate cortex, cMFG caudal middle frontal gyrus, CUN cuneus, ENT entorhinal cortex, FUS fusiform gyrus, IPL inferior parietal cortex, ITG inferior temporal gyrus, iCC isthmus cingulate cortex, LOG lateral occipital cortex, LOF lateral orbitofrontal cortex, LING lingual gyrus, MOF medial orbitofrontal cortex, MTG middle temporal gyrus, PARH parahippocampal gyrus, paraC paracentral, lobule, pOPER pars opercularis of inferior frontal gyrus, pORB pars orbitalis of inferior frontal gyrus, pTRI pars, triangularis of inferior frontal gyrus, periCAL pericalcarine cortex, postC post-central gyrus, PCC posterior, cingulate cortex, preC precentral gyrus, PCUN precuneus, rACC rostral anterior cingulate corte, rMFG rostral, middle frontal gyrus, SFG superior frontal gyrus, SPL superior parietal cortex, STG superior temporal gyrus, SMAR supramarginal gyrus, FP frontal pole, TP temporal pole, TT transverse temporal gyrus, INS insula. L left, R right