Figure 3.
New H2A.X Accumulation at UV Sites and Replication Foci Is Coupled to DNA Synthesis
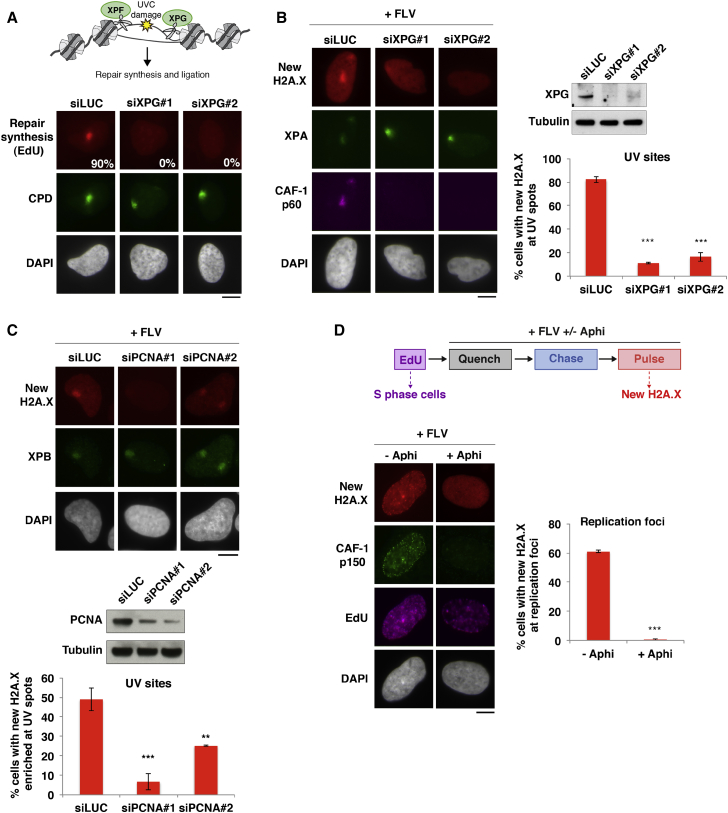
(A) Scheme: XPG’s role in the late steps of UVC damage repair. Percentage of cells showing repair synthesis (EdU) at UVC-damage sites (CPDs [cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers]) in U2OS cells treated with the indicated siRNAs (siLUC, control). At least 200 cells were scored in 2 independent experiments.
(B and C) New H2A.X accumulation at UVC damage sites marked by XPA or XPB analyzed 2 hr after irradiation in the presence of flavopiridol (+FLV) in U2OS H2A.X-SNAP cells treated with siRNAs targeting XPG (B) or PCNA (C) (siLUC, control). Knockdown efficiencies are verified by western blot and by impaired CAF-1 recruitment to damage sites.
(D) New H2A.X accumulation at replication foci (marked by EdU before aphidicolin addition) in U2OS H2A.X-SNAP cells treated with flavopiridol (+FLV) and the replication inhibitor aphidicolin (Aphi). Replication inhibition is shown by impaired CAF-1 recruitment to EdU foci.
Bar charts show mean ± SD from at least 2 independent experiments. Scale bars, 10 μm. ns, non-significant; ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001. See also Figure S4.