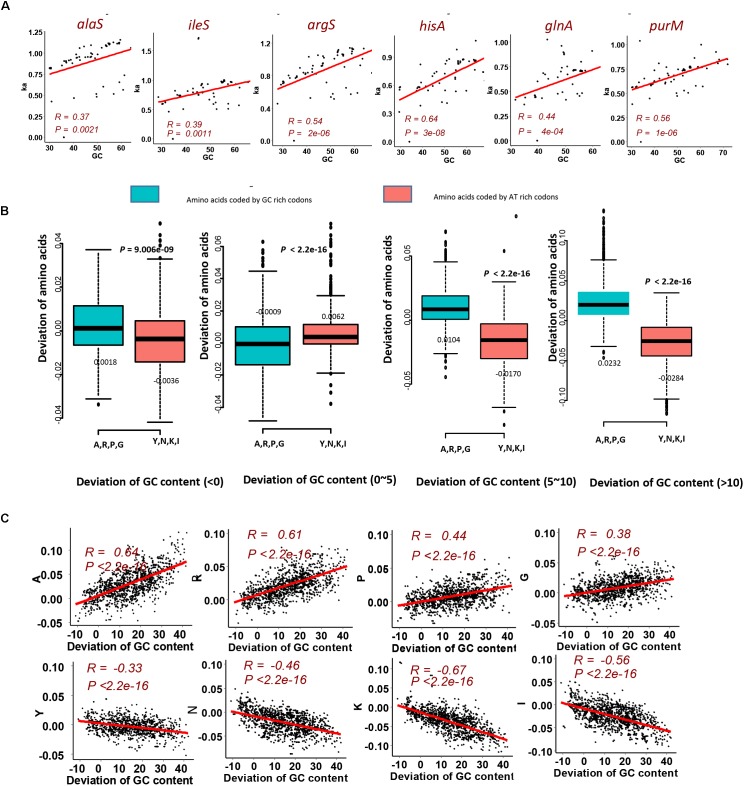
FIGURE 2.
GC content significantly contributes to the LUCA protein evolution. (A) Evolutionary rate (Ka) for six genes homologous to the LUCA genes from multi genomes positively correlates with corresponding GC content. Higher GC content happens with higher Ka value. The red points are genes from MmarS2. (B) The gain and loss tendency of amino acids encoded by the GC rich/AT rich codons under different GC deviations. We used the GC content of one gene to minus the GC content of its homologous gene in MmarS2, and then we acquire the deviation of GC content. The deviation of amino acids is the amino acid frequencies of one gene minus the amino acid frequencies of its homologous gene in MmarS2. More details can be found in the part of Section “Materials and Methods.” (C) The correlation between the deviation of GC content and the deviation of amino acid composition. Amino acids A, R, P, and G are encoded by GC rich codons, while amino acids Y, N, K, and I are encoded by AT rich ones.