Figure 1.
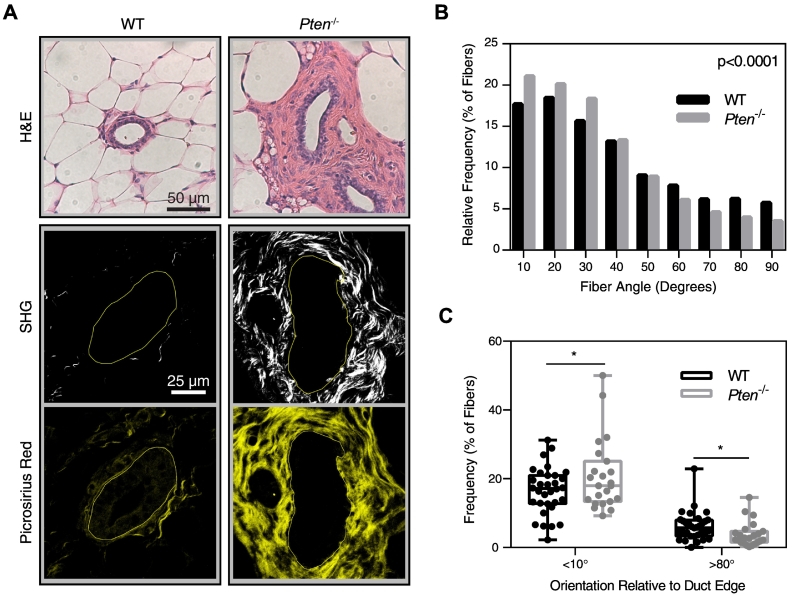
Pten knockout affects collagen alignment in vivo. (A) H&E staining, second harmonic generation, and picrosirius red staining of representative ducts within murine mammary gland tissue sections. SHG images are shown above their corresponding picrosirius red image. Solid lines represent the lumen edge. (B) Histogram of collagen fiber angle relative to the duct, quantified using CurveAlign software. Bin size = 10°. P value represents the probability of the WT and Pten−/− histograms originating from the same distribution. (C) Plot of the fraction of fibers oriented at <10° or >80° relative to the duct edge. Each dot represents the fraction of fibers surrounding an individual duct. WT: n=32. Pten−/−: n=23, where n represents the number of ducts imaged from 7 and 5 mice, respectively. *P<.05, **P<.01.