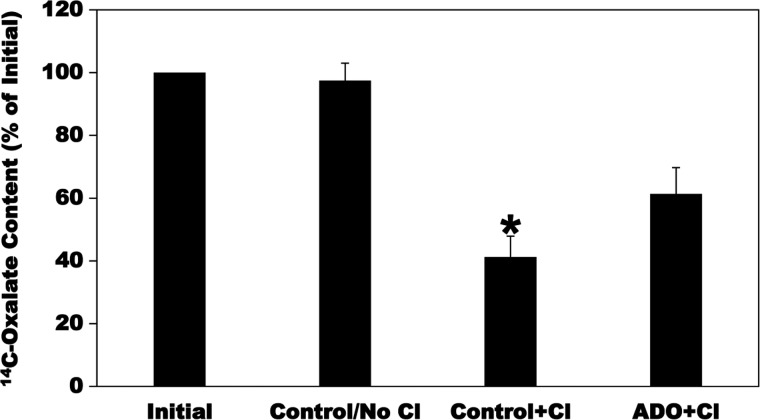
Fig. 3.
Effect of adenosine (ADO) on [14C]oxalate efflux by Caco2-BBE (C2) cells. C2 cells were first preloaded with radioisotope by incubating for 6 min in Cl-free uptake buffer containing 20 µM [14C]oxalate. The [14C]oxalate preloading was terminated by 2–3 rapid washes of the cell monolayers with Cl-free solution. The C2 cells were then treated with vehicle (Control) or ADO for 2 min, followed by 2 rapid washes of the cell monolayers with Cl-free solution. The C2 cells were then reincubated for 10 min in the Cl-free buffer without (Control/No Cl) or isotonic replacement of gluconate with 10 mM Cl (Control + Cl and ADO + Cl). The C2 [14C]oxalate contents were measured at the end of the 6-min preloading period (Initial) and after 10-min reincubation, and net efflux was calculated as described in materials and methods. Values are means ± SE of 4 independent experiments each of which was done in duplicate or triplicate and was normalized to the Initial value. ADO significantly reduced the Cl-induced [14C]oxalate efflux (*P < 0.001, < 0.001, and < 0.05 for Control + Cl compared with Initial, Control/No Cl, and ADO + Cl, respectively, by ANOVA).