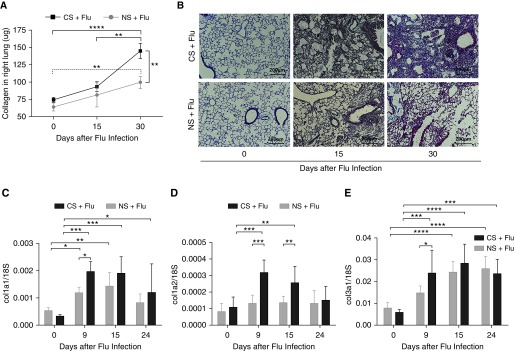
Figure 2.
CS exposure exacerbates lung fibrosis during influenza virus infection. Wild-type mice were exposed to CS for 2 weeks and then infected with 10 pfu of influenza virus. Smoking continued after viral infection. (A) The collagen content in the right lung was measured by Sircol assay on Days 15 and 30 after infection. Lungs were harvested from influenza-infected mice that were either exposed to smoke or remained in room air at the indicated time points. (B) Lung sections were subjected to Masson’s trichrome staining, and representative sections from three independent experiments are shown at a total magnification of ×40. The expression of collagen-related genes was measured on Days 9, 15, and 24 after infection. Scale bars: 200 μm. (C–E) Expression of collagen 1a1 (col1a1) (C), col1a2 (D), and col3a (E) was normalized with the expression of 18S in the lung tissue. Data are from one of at least three independent experiments performed with n = 4–6 in each group at each given time point. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.