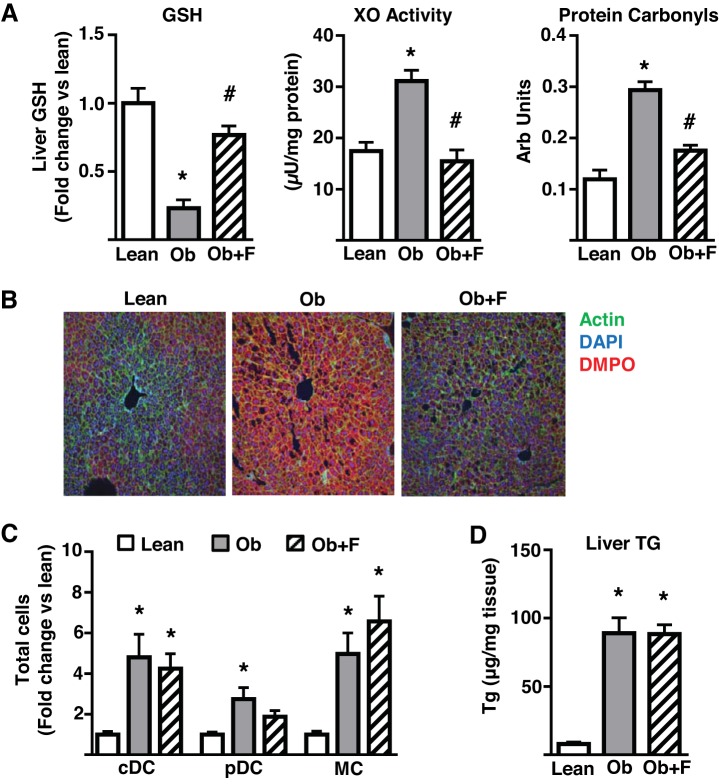
Fig. 7.
The effects of lowered oxidative stress on obesity-induced hepatic DC/MC accumulation. Male mice were fed either a control (Lean) or a high-fat (Ob) diet for 20 wk. Mice treated with febuxostat (Ob + F) were fed similarly to Ob mice but were provided febuxostat (50 mg/l) in their drinking water for the final 7 wk of the study. A: glutathione (GSH), xanthine oxidase (XO) activity, protein carbonyls. B: representative immunofluorescence images of liver biomolecular free radical adducts assessed by immuno-spin trapping following intraperitoneal injections of 5-Dimethyl-1Pyrroline-N-Oxide (DMPO) 24, 12, and 6 h before euthanasia (n = 7 all groups); C: liver dendritic cells (cDC, pDC), and monocyte/macrophage (MC) populations as assessed by flow cytometry (n = 6 all groups); D: liver triglyceride levels (TG; n = 5–7). All plots represent mean ± SE and significant differences are indicated (*P < 0.05 Ob vs. Lean; #P < 0.05 Ob + F vs. Ob). cDC, conventional DC; DC, dendritic cell; pDC, plasmacytoid DC; TG, triglyceride.