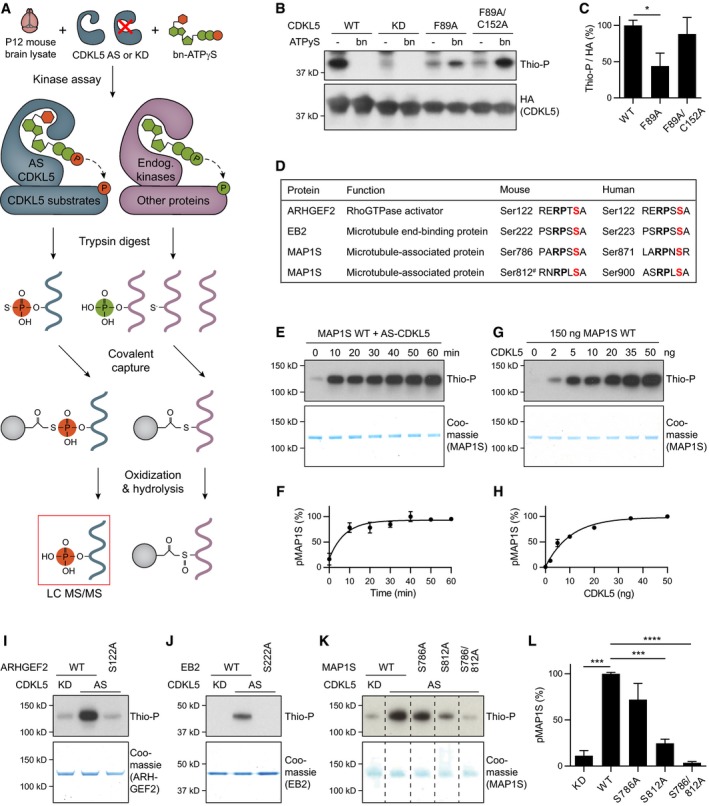
-
A
Schematic of chemical genetic kinase substrate identification method. AS‐CDKL5 utilizes benzyl‐ATPγS to thiophosphorylate its substrates. Following trypsin digest, thiol‐containing peptides are captured on iodoacetyl agarose beads. Thiophosphate ester linked peptides are released by oxone induced hydrolysis while cysteine‐containing peptides remain attached. Eluted phosphopeptides are analysed with liquid chromatography‐tandem mass spectrometry (LC‐MS/MS).
-
B, C
CDKL51–352 autophosphorylation is shown. WT CDKL5 uses ATPγS, KD is inactive, F89A uses benzyl‐ATPγS with reduced efficiency, F89A/C152A mutant has rescued activity. Quantification of Thio‐P signal is normalized for CDKL5 levels (HA), and KD background is subtracted. Fisher's LSD: n = 4 replicates. bn, benzyl.
-
D
A list of novel CDKL5 substrate targets and phosphorylation sites identified. All phosphorylation sites are conserved in human. # MAP1S pS812 is identified based on sequence homology. Red = phosphorylated serine, bold = RPXS consensus sequence.
-
E–H
In vitro kinase assays showing efficient MAP1S phosphorylation by CDKL5. 50 ng (40 nM) AS‐CDKL5 phosphorylates 150 ng (50 nM) MAP1S very rapidly (E, F). In 30 min of incubation, 150 ng MAP1S is phosphorylated by small amounts of CDKL5 (G, H). Quantification of phosphorylated MAP1S is normalized to maximum intensity. n = 2 replicates.
-
I–L
Western blots of in vitro kinase assays showing loss of phosphorylation in phosphomutants ARHGEF2 S122A (I), EB2 S222A (J) and MAP1S S786/812A (K). Substrate levels are shown by Coomassie staining underneath. MAP1S phosphorylation is quantified in (L). Dunnett's multiple comparison: n = 3 replicates.
Data information: Thio‐P, anti‐thiophosphate ester antibody; n.s., not significant, *
P < 0.05, ***
P < 0.001, ****
P < 0.0001, error bars are SEM. In panel (K), non‐relevant lanes have been removed for simplicity (see accompanying Source Data for full blot).
Source data are available online for this figure.