Figure 5. Mass spectrometric validation of DLG5 as a CDKL5 substrate.
-
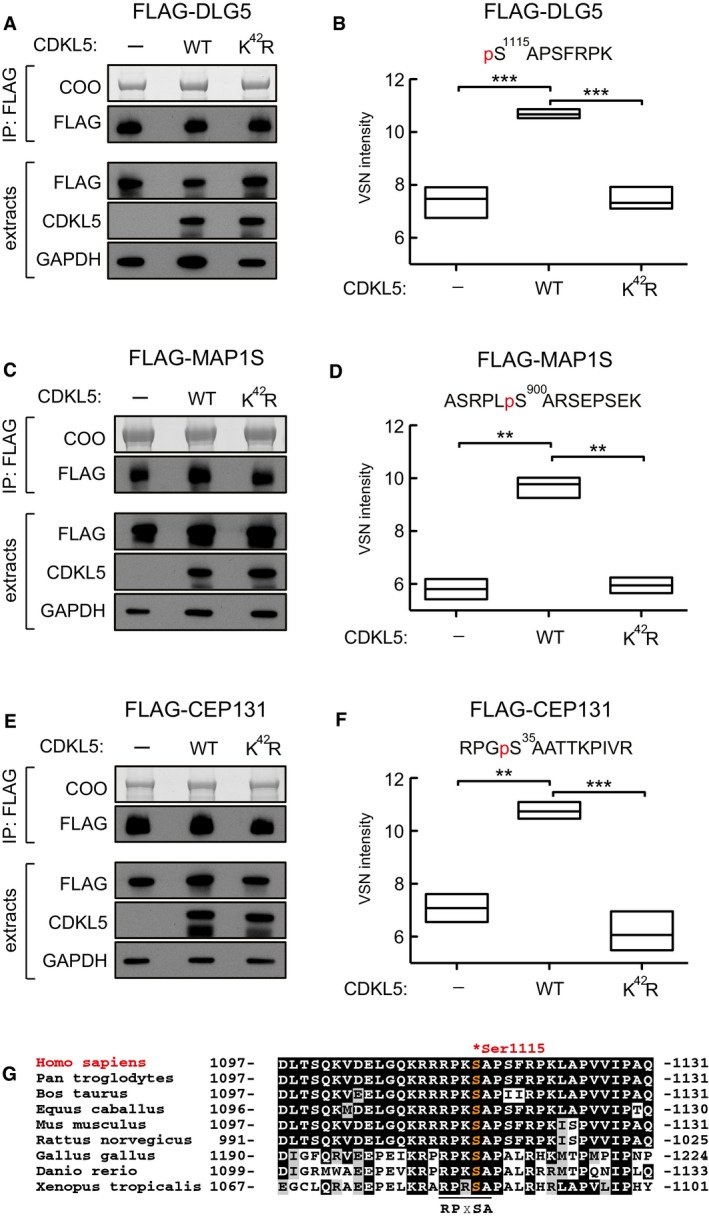
A–FTesting CDKL5‐dependent DLG5 phosphorylation in cells. HEK293 cells were co‐transfected with FLAG‐DLG5 (A, B), FLAG‐MAP1S (C, D) or FLAG‐CEP131 (E, F) together with either empty vector (−), wild‐type CDKL5 (WT) or kinase‐dead CDKL5 (K42R). Cells were harvested after 24 h and lysed, and extracts were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti‐FLAG‐agarose beads. Precipitates were resolved by SDS–PAGE and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue (COO, top panel). A small fraction of the precipitates was subjected to Western blotting with anti‐FLAG antibodies (A, C). The input extracts were also subjected to immunoblotting with the antibodies indicated in the lower panels. Three independent experiments were done, and one representative experiment is shown. Coomassie‐stained bands as shown in top panels of (A, C and E) were excised, destained and proteins digested. Peptides were extracted, TMT labelled and analysed using mass spectrometry. VSN‐calibrated and transformed, isotopically corrected reporter ion intensities of the phosphopeptides of interest are plotted in (B, D and F); the outline of the box plot indicates minimum and maximum values, and the middle line indicates the median. Higher intensity corresponds to higher phosphopeptide abundance in the relevant sample. Statistical testing was carried out using a t‐test (Computer Code EV1; Appendix Fig S4); to account for multiple testing, the significance threshold was adjusted from α = 0.05 to α = 0.00833 (six t‐tests) by Bonferroni correction (Computer Code EV1). All t‐tests resulted in a P‐value below the adjusted significance threshold. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. Individual P‐values are shown in Table EV3.
-
GSequence alignment of the Ser1115 phosphorylation site in DLG5 in the species indicated.
Source data are available online for this figure.
