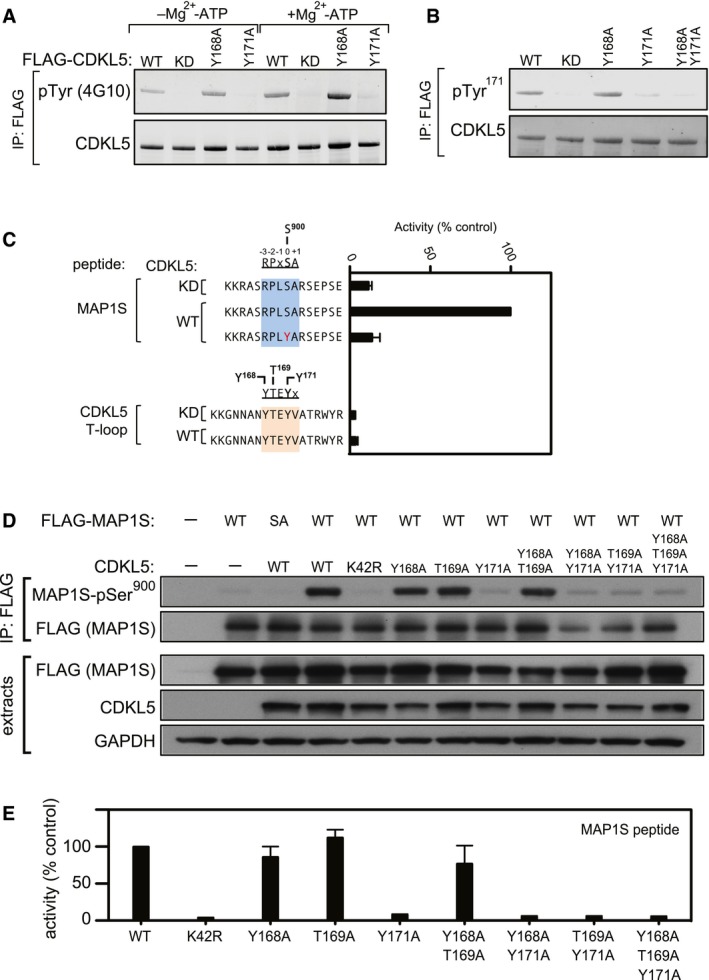
Figure 6. T‐loop autophosphorylation is critical for CDKL5 activity.
-
A, BTyr‐autophosphorylation of CDKL5. Anti‐FLAG precipitates from HEK293 cells transiently expressing FLAG‐tagged CDKL5 (wild type “WT” or mutants K42R kinase‐dead “KD”, Y168A,Y171A or both) were subjected to immunoblotting with the antibodies indicated before or after incubation of precipitates with Mg2+‐ATP for 30 min at 30°C. Each experiment was done three times, and a representative experiment is shown.
-
CCDKL5 cannot phosphorylate Tyr‐containing synthetic peptides. Anti‐FLAG precipitates from HEK293 cells transiently expressing FLAG‐tagged CDKL5 (wild type “WT” or a K42R kinase‐dead “KD” mutant) were incubated with the synthetic peptides indicated in the presence of [γ‐32P]‐labelled ATP‐Mg2+, and peptide phosphorylation was measured by Cerenkov counting. Data are represented as mean ± SEM from three independent experiments.
-
HHEK293 cells were co‐transfected with untagged CDKL5 (wild type “WT” or the mutants indicated) and FLAG‐tagged MAP1S [wild type (WT), a Ser900Ala mutant (SA)] or empty vector (−). Anti‐FLAG precipitates were subjected to Western blotting with the antibodies indicated. The input extracts were also subjected to immunoblotting (lower panels). Each experiment was done three times, and a representative example is shown.
-
IAnti‐FLAG precipitates from HEK293 cells transiently expressing FLAG‐tagged CDKL5 (wild type “WT” or the mutants indicated) were incubated with a synthetic peptide corresponding to the sequence around the MAP1S Ser900 phosphorylation site, in the presence of [γ‐32P]‐labelled ATP‐Mg2+. Peptide phosphorylation was quantitated in a scintillation counter. Data are represented as mean ± SEM from three independent experiments.
Source data are available online for this figure.
