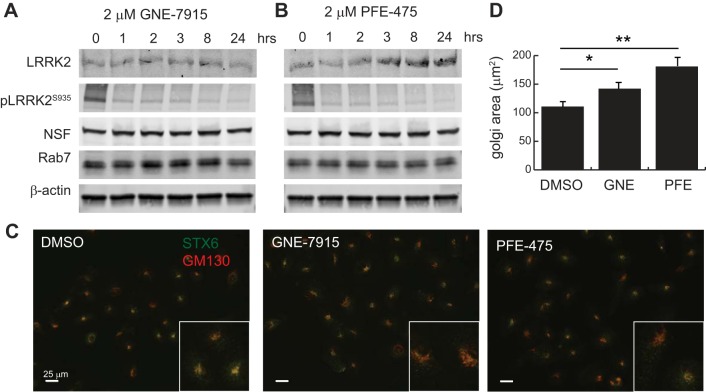
Fig. 2.
Pharmacologic inhibition of LRRK2 kinase activity causes abnormal Golgi compartment enlargement. A and B: wild-type HK2 cells were treated with the catalytic LRRK2 inhibitors GNE-7915 and PFE-475 for the indicated times to demonstrate prolonged inhibition of LRRK2 activity, as demonstrated by S935 autophosphorylation. Protein levels of NSF, Rab7, and β-actin levels are unchanged by LRRK2 enzymatic inhibition. C: representative immunofluorescent images of HK2 cells treated with LRRK2 inhibitors and then stained with antibodies for gm-130 (red) and STX6 (green) to demonstrate increase in Golgi area after LRRK2 inhibition. D: quantification of gm130-positive Golgi apparatus area in normal HK2 cells after 1-h treatment with 5 nM nocodazole or DMSO vehicle. E: quantification of gm130-positive Golgi apparatus area in normal HK2 cells after 24 h treatment with 2 μM concentration of the indicated LRRK2 inhibitor or DMSO vehicle. Error bars indicate standard deviation of triplicate or quadruplicate experimental replicates (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.005). LRRK2, leucine-rich repeat kinase 2; HK2, normal human kidney cells; NSF, N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein; STX, syntaxin.