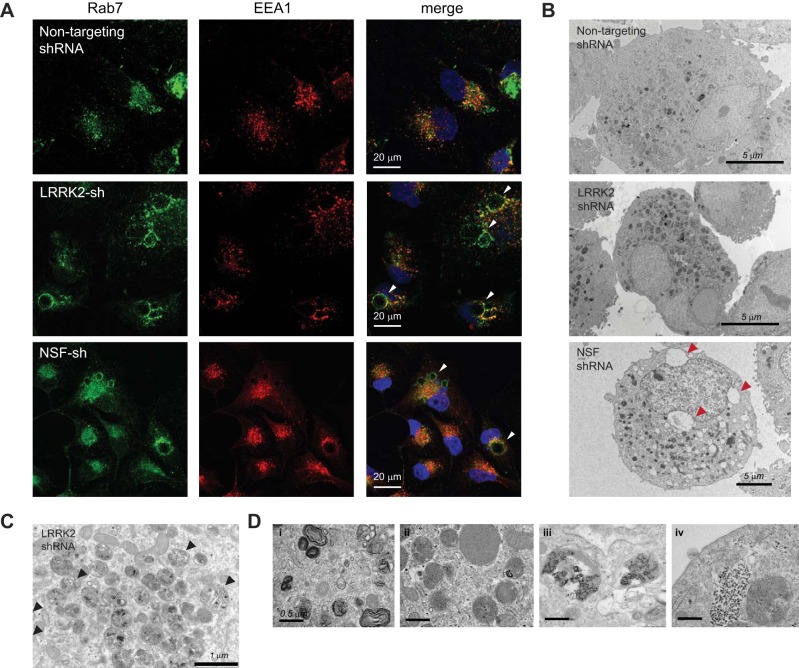
Fig. 3.
Depletion of NSF phenocopies LRRK2 deficiency and results in the accumulation of vesicular waste cargo. A: confocal immunofluorescent images of HK2 cells transduced with nontargeting shRNAs or shRNAs targeted to LRRK2 or NSF. Cells were stained with antibodies for endogenous EEA1 (red) and Rab7 (green) to indicate the early and late endosomal compartments, respectively. DAPI (blue) costain of nuclei is also shown in the merged image. B–D: transmission electron microscopy was performed on dissociated cell pellets of HK2 cells that were stably depleted of LRRK2 or NSF using lentiviral shRNAs. B: whole cell images of stable lines showing the accumulation of electron-dense vesicles in HK2 cells after depletion of LRRK2 or NSF. Cells also displayed large vacuolar inclusions in some instances (red arrows). C: vesicles in HK2 cells lacking LRRK2 display whole organelles encased in vesicles (black arrows), which suggest that some of these vesicles may be autophagic in origin. D: higher magnification images of LRRK2-deficient HK2 cells demonstrate the variety of waste cargo in vesicles, which includes: 1) membrane whorls, 2) lipid droplets, and 3–4) electron dense aggregates of undetermined identity. LRRK2, leucine-rich repeat kinase 2; HK2, normal human kidney cells; NSF, N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein; shRNA, short hairpin RNA.