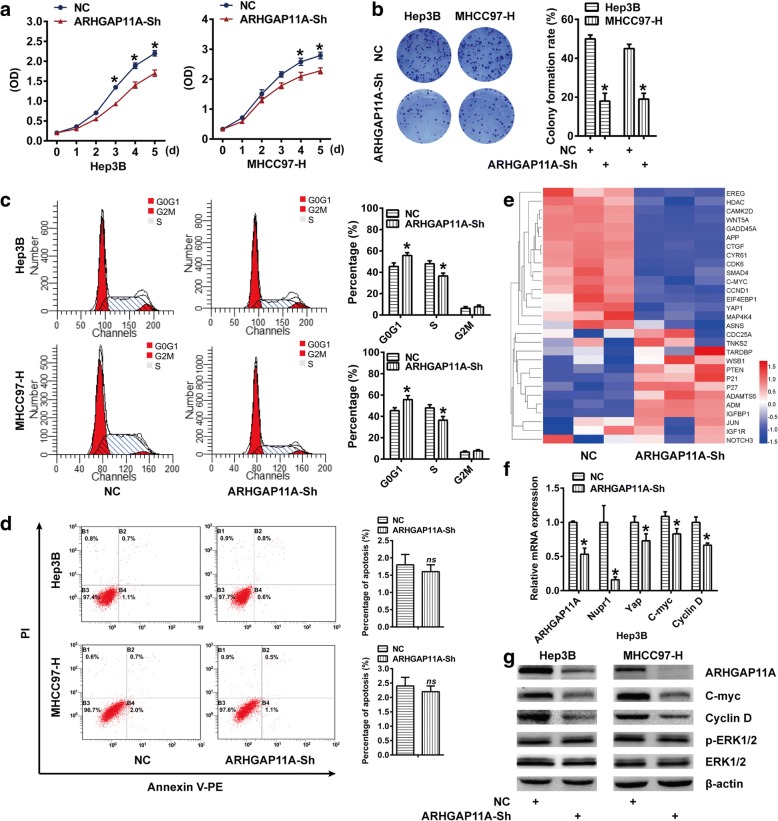
Fig. 2.
ARHGAP11A is indispensable for HCC cell proliferation, but not apoptosis, in vitro. Columns or curves, mean (n = 3, in triplicate); bars, SD. *, P < 0.05 versus NC. ns, no significance. a Hep3B and MHCC97-H cells were stably infected with Scrambled (NC) or ARHGAP11A-Sh and cultured for 1–5 days. Cell proliferation was detected by a CCK8 assay. b The colony forming ability of Hep3B and MHCC97-H cells following ARHGAP11A knockdown. c ARHGAP11A knockdown arrested the cell cycle in G0/G1 phase. d Flow cytometry was used to assess apoptosis in ARHGAP11A-Sh cells or NC. e Heatmap showing the differential expression of genes involved in cell proliferation upon ARHGAP11A knockdown (n = 3, triplicate). f Relative mRNA expression of ARHGAP11A, Nupr1, Yap, C-myc and Cyclin D determined by qRT-PCR analysis in ARHGAP11A-Sh or NC Hep3B cells. g Protein expression of ARHGAP11A, C-myc, Cyclin D, p-ERK1/2 and ERK1/2 in one experiment, representative of three