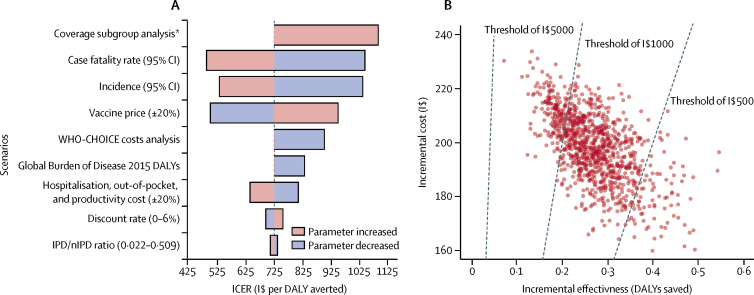
Figure 5.
Results of one-way parameter scenario and probabilistic sensitivity analyses
(A) One-way sensitivity analysis was done to test the robustness of the economic model by varying key parameters over plausible ranges (shown in parentheses) to assess their global effect on ICER and number of deaths. Bars represent the median ICER generated from 1000 bootstraps. Longer bars represent greater sensitivity of the global results to variations in that key parameter. (B) In the probabilistic sensitivity analysis diagram, each point represents the result of the incremental cost (y-axis), and effectiveness (x-axis) of one bootstrap sample on the global scale. A total of 1000 bootstraps were generated. 100% of the simulations resulted in a positive ICER (quadrant 1). Dotted lines indicate willingness-to-pay thresholds of I$500, $1000, and $5000 per DALY saved. Points to the right of each dotted line are cost-effective at that willingness-to-pay threshold. CI=credible interval. DALY=disability-adjusted life-year. ICER=incremental cost-effectiveness ratio. IPD=invasive pneumococcal disease. nIPD=non-invasive pneumococcal disease. I$=international dollars. *In the coverage subgroup analysis, 63 countries without national immunisation programmes or with three-dose diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis coverage of less than 70% were excluded.