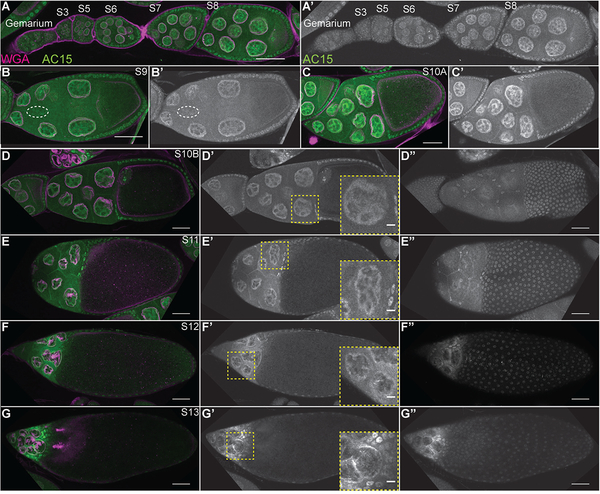
Figure 9:
AC15 nuclear actin is present in all nuclei from mid-oogenesis. (A-G”) Maximum projections of 2–4 slices of confocal stacks of the indicated stages of wild-type (yw) follicles; insets in D’-G’ are a zoomed in image of the yellow boxed region. (A-G) Magenta = Wheat germ agglutinin (WGA, marks nuclear envelope), Green = AC15. (A’-G’ and D”-G”) White = AC15. AC15 nuclear actin is weak during early oogenesis (germarium-S5, A-A’). During S6–8, AC15 nuclear actin is weak but increasing with development in both the nurse cells and follicle cells (A-A’); nurse cell levels appear higher than the follicle cells at these stages. This increase in AC15 nuclear actin continues during S9–10A (B-C’). Within the nurse cells, the AC15 nuclear actin is structured and is enriched at the nuclear periphery (B-C’). During S10B-12, the level of AC15 nuclear actin remains high, but becomes more restricted to the nuclear periphery in the nurse cells (D-F’, insets are zoomed in images of nurse cells). At S13, AC15 nuclear actin is strongly reduced and AC15 labels cytoplasmic actin (G-G’, inset is zoomed in image of nurse cells). AC15 nuclear actin also increases with development in the follicle cells (A-C’). AC15 nuclear actin is weak within the migrating border cells during S9 (B-B’, border cells circled by white dashed line). AC15 also labels both the main body (those over the oocyte) and stretch follicle cells (those over the nurse cells) throughout the end of oogenesis (D”-G”). Scale bars = 50μm, except in the insets in D’-G’ where scale bars = 10μm.