Figure 1.
Cortical Stroke Induces a Spatial and Temporal Multilineage Response from Nestin-GFP Precursor Cells
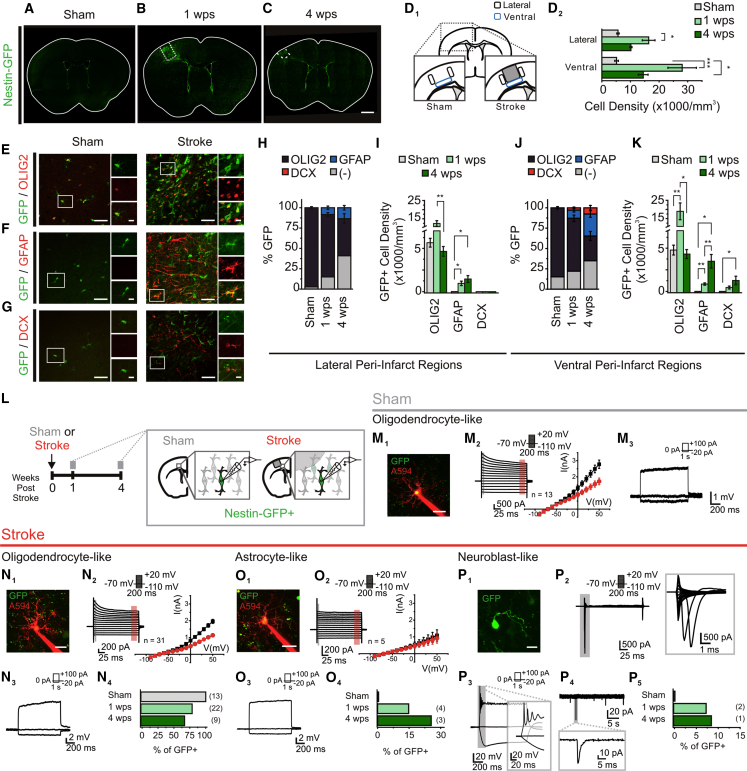
(A–C) GFP cells in the Nestin-GFP mouse following sham surgery (A), or 1 week (1 wps) (B) and 4 weeks (4 wps) (C) after cortical stroke.
(D) Schematic of quantification regions in the sham and stroke-injured cortex (D1), and quantification of GFP+ cell density (D2). ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗∗p < 0.0005; p < 0.001, Kruskal-Wallis test; n = 5 mice/group.
(E–G) Immunostained sham mouse cortex (left panel) and stroke-injured ventral peri-infarct cortex at 1 wps (right panel) of GFP with OLIG2 (E), GFAP (F), and DCX (G).
(H and I) Proportion (H) and density (I) of GFP+ cells in the lateral peri-infarct cortex. The proportion of GFP/OLIG2+ cells was ∼97% in sham mice, and decreased post stroke. p < 0.0001; p < 0.05 versus 1 wps; p < 0.0001 versus 4 wps, one-way ANOVA. GFP/GFAP+ cells were only observed after stroke (1 wps: p < 0.05; 4 wps: p < 0.05, versus sham; one-sample t test versus test mean), but their proportion did not change between 1 and 4 wps. GFP/OLIG2+ density showed a non-significant increase at 1 wps (versus sham), with a significant decrease observed at 4 wps (p < 0.01 versus 1 wps; overall, p = 0.001, Kruskal-Wallis test). GFP/GFAP+ cells were only present post stroke (1 wps: p < 0.05; 4 wps: p < 0.05, versus sham; one-sample t test versus test mean). No GFP/DCX+ cells were observed (n = 3–7 mice/group).
(J and K) Proportion (J) and density (K) of GFP+ cell types in the ventral peri-infarct cortex. The proportion of GFP/OLIG2+ cells showed a trend toward decreasing at 1 wps (p = 0.054), and was significantly less at 4 wps (p < 0.001), in comparison with sham (p < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA). GFP/GFAP+ cells were only observed after stroke (1 wps: p < 0.05; 4 wps: p < 0.01, versus sham; one-sample t test versus test mean), and their proportion increased from 1 to 4 wps (p < 0.05, t test). GFP/DCX+ cells were only present post stroke (1 wps: p < 0.05; 4 wps: p < 0.05, versus sham; one-sample t test versus test mean). GFP/OLIG2+ density increased at 1 wps (p = 0.01; p < 0.05 versus sham), but returned to sham levels by 4 wps (p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA). GFP/GFAP+ cells only appeared post stroke (1 wps: p < 0.01; 4 wps: p < 0.05 versus sham; one-sample t test versus test mean), and their density increased from 1 to 4 wps (p < 0.05, t test). GFP/DCX+ cells only appeared post stroke (significant at 4 wps: p < 0.05 versus sham; one-sample t test versus test mean; n = 3–7 mice/group).
(L) Schematic of experiment.
(M) Properties of cortical GFP cells from sham mice. (M1) Two-photon (2P) image of a GFP cell filled with Alexa 594. (M2) Current traces responding to voltage steps, and I-V graph of the amplitude at 5 ms (black, black highlight on trace) and 180–190 ms (red, red highlight on trace) from voltage step onset. (M4) Voltage traces, responding to current steps.
(N) Properties of the first peri-infarct GFP population that resemble the cells observed in the sham cortex. (N1) 2P image of a GFP cell filled with Alexa 594. (N2) Current traces responding to voltage steps, and I-V graph of the amplitude at 5 ms (black, black highlight on trace) and 180–190 ms (red, red highlight on trace) from voltage step onset. (N3) Voltage traces, responding to current steps. (N4) Proportion of cells with observed electrophysiological phenotype.
(O) Properties of the non-excitable second GFP population. (D1) 2P image of a GFP cell filled with Alexa 594. (O2) Current traces responding to voltage steps, and I-V graph of the amplitude at 5 ms (black, black highlight on trace) and 180–190 ms (red, red highlight on trace) from voltage step onset. (O3) Voltage traces responding to current steps. (O4) Proportion of cells with observed electrophysiological phenotype.
(P) Properties of the excitable third GFP population. (P1) 2P image of a GFP cell. (P2) Current traces responding to voltage steps, showing fast inward current. (P3) Voltage traces, responding to current steps, showing the presence of APs. (P4) Current traces of sPSCs (Vh, −70 mV). (P5) Proportion of cells with observed electrophysiological phenotype.
Scale bars, 1 mm (mosaic) (A–C), 20 μm (insets); 40 μm (E–G), 10 μm (insets); 20 μm (M1, N1, and O1); 10 μm (P1). Data: mean ± SEM. See also Figure S1.