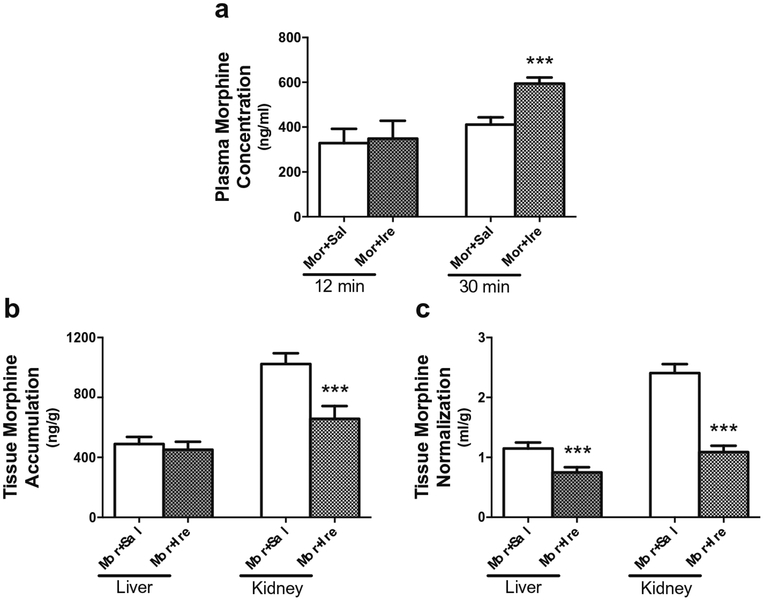
Fig. 4. Effect of irinotecan on the plasma concentrations and tissue accumulation of morphine in mice.
(a) The plasma concentrations of morphine in the mice administrated with irinotecan or saline. Mice at age of 10–12 weeks were randomly divided into 2 groups and injected intraperitoneally with 45 mg/kg irinotecan (n = 6) and 0.9% saline (n = 6), respectively. Thirty minutes later, all mice were given 1.45 mg/kg of morphine (3H-morphine: unlabeled morphine = 1:10000). The blood samples were collected at 12 min and 30 min after morphine injection. (b) Comparison of liver and kidney accumulation of morphine between the mice administrated with saline plus morphine and those with irinotecan plus morphine. The tissues were isolated at 30 min after morphine injection. (c) Comparison of liver and kidney accumulation of morphine between the two groups, as that in (b), after normalization by the terminal plasma concentration. ***P < 0.001, significantly different in the mice received with irinotecan as compared with those received saline control.