Fig. 3.
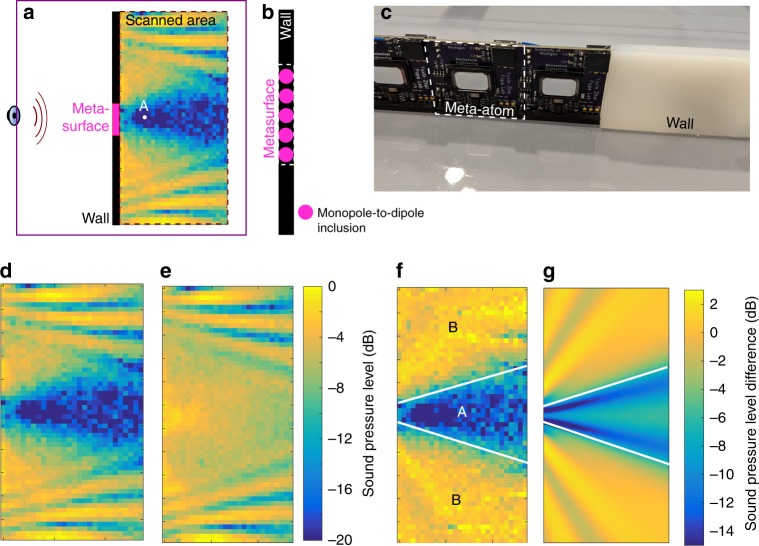
Experimental setup and performance. a A speaker placed on the edge of a two-dimensional acoustic waveguide sends acoustic waves inside the waveguide towards a polycarbonate wall 6 mm thick. The bianisotropic metasurface replaces a wall section 17.5 cm long in the middle of the wall. The sound pressure distribution is measured in a 110 cm by 50 cm region placed immediately behind the wall. The region shows the measured sound pressure level at 3000 Hz obtained with the activated metasurface. Point A is situated 10 cm behind the metasurface. b The metasurface is composed of five meta-atoms placed side by side. Each meta-atom simulates a monopole-to-dipole inclusion embedded into the polycarbonate wall. c Photo of metasurface and wall. The monopole-to-dipole meta-atom is highlighted. d Sound pressure level (SPL) measured at 3000 Hz with the bianisotropic response activated (αmd ≠ 0) and e deactivated (αmd = 0). f SPL difference between the activated and deactivated states. The sound suppression level (SSL) is defined as the difference between the average SSLs computed in regions A and B. g Numerically simulated SPL difference for an infinitely stiff and dense wall