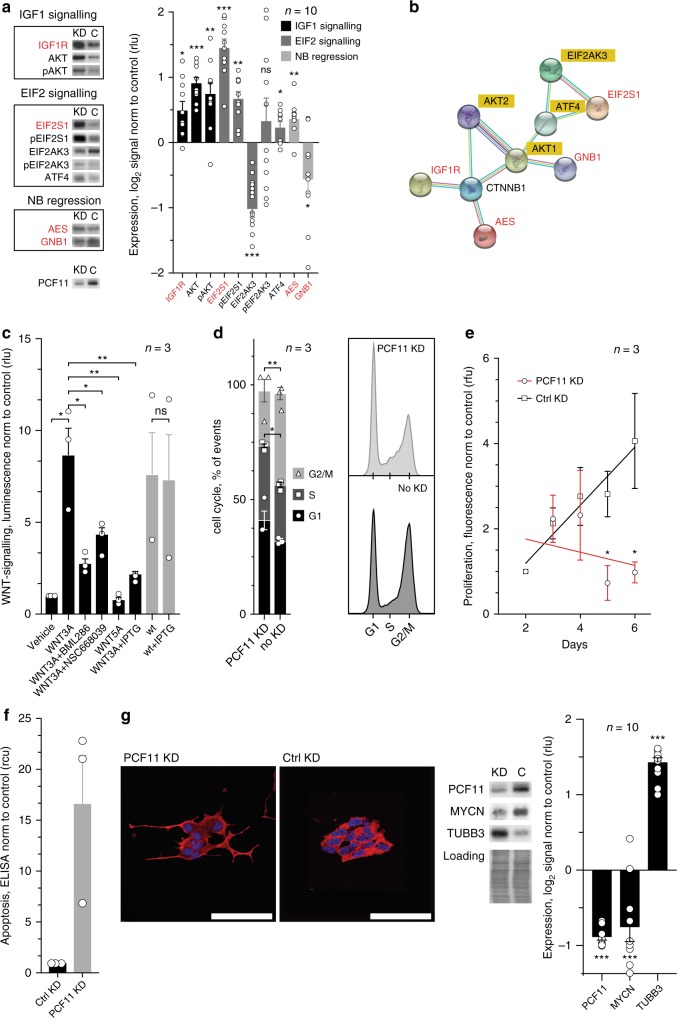
Fig. 4.
PCF11-directed APA regulation converges on WNT signalling and modulates cell cycle progression, proliferation, apoptosis and neuronal differentiation. a Effect of PCF11-mediated APA regulation on protein expression of APA-affected targets (red) and downstream signalling pathways compared to a control knockdown. b Protein-protein interaction network of validated APA-affected candidates (red) impinging on WNT signalling (i.e. CTNNB1, bold; String-DB). This corresponds to the predicted function of the entire cohort of APA-affected genes with a role in neurodifferentiation (compare Supplementary Figure 6a). c shRNA-mediated depletion of PCF11 induced by IPTG (see Methods section) inhibits canonical WNT signalling in reporter assays (compare bar 2 with 6). WNT antagonists BML286 and NSC668039, and WNT5A (a non-canonical WNT-ligand) confirm specificity of pathway activation and functionality of the beta-catenin TCF/LEF-driven gene-reporter construct, respectively (for PCF11-APA-directed regulation of WNT signalling and its specific control via different transcript isoforms encoding GNB1 see endogenous TCF7 expression in Fig. 6e). PCF11 depletion results in d cell cycle retardation, e reduced proliferation, f increased apoptosis (ELISA-DNA fragmentation assay; n = 3; a loss-of-apoptosis phenotype upon PCF11 overexpression is shown in Supplementary Figure 6b) and g triggers neuroblastoma differentiation morphologically and molecularly (for PCF11 depletion-induced neuronal differentiation of neuroblastic CHP-134 cells see Supplementary Figure 6c). Error bars in a–g show mean ± s.e.m. of at least three independent experiments, one-sided t-test p-value; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; FC fold change, cells are stained with an antibody directed against TUBB3 (red), nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue)