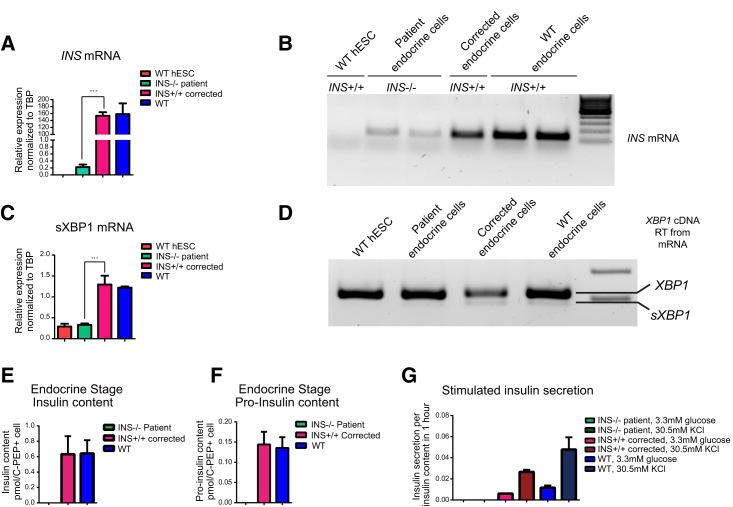
Figure 3.
Gene Correction Restores Insulin Expression and Insulin mRNA Stability and Increases Spliced XBP-1
(A) INS mRNA quantitation results by qRT-PCR for INS mutant β-like cells in comparison with corrected and wild-type cells. n = 3 independent experiments. Data represent mean ± SD (∗∗∗p < 0.001). hESC, human ESC; TBP, TATA-box binding protein; WT, wild-type.
(B) Agarose gel electrophoresis results for insulin mRNA after qRT-PCR.
(C) Spliced XBP1 (sXBP1) mRNA quantitation results by qRT-PCR for INS mutant β-like cells in comparison with corrected and wild-type cells. n = 3 independent experiments. Data represent mean ± SD (∗∗∗p < 0.001).
(D) RT-PCR results for XBP1 and sXBP1 mRNA using agarose gel electrophoresis.
(E) Analysis of insulin content using ELISA for INS mutant, corrected, and WT β-like cells. n = 3 independent experiments.
(F) Analysis of pro-insulin content using ELISA for INS mutant, corrected, and WT β-like cells. n = 3 independent experiments.
(G) Analysis of insulin secretion in INS mutant and corrected β-like cells using ELISA. Insulin secretion was analyzed under 3.3 mM glucose and 30.5 mM KCl conditions. n = 3 independent experiments. Significance was tested by Student’s t test.