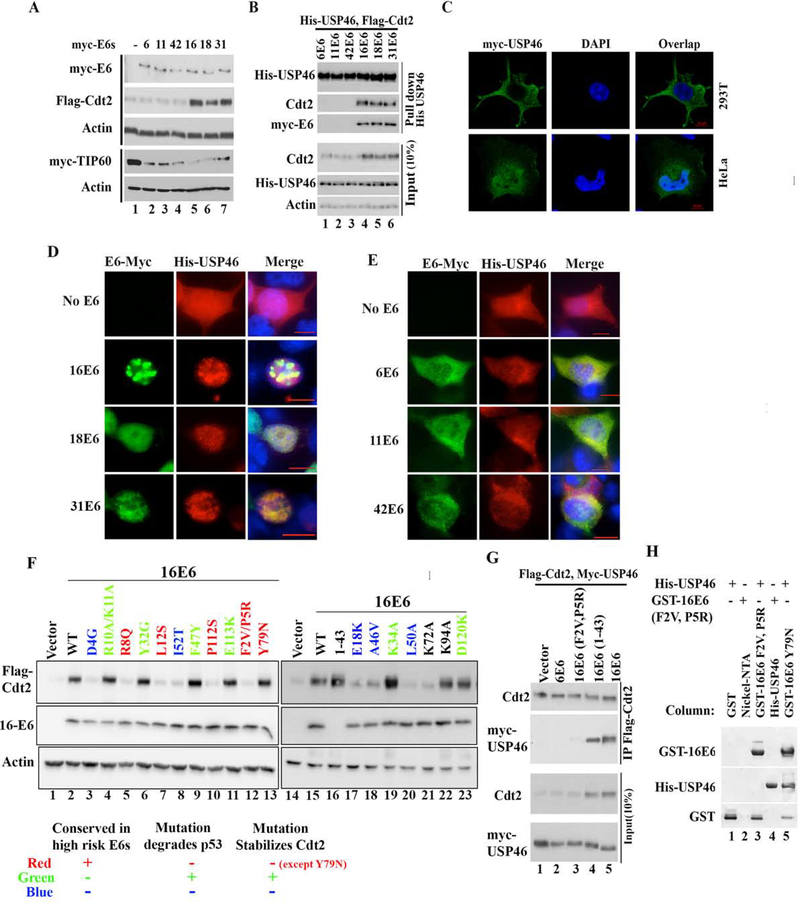
Figure 4: E6 oncoproteins from high risk HPVs translocate cytoplasmic USP46 into nucleus and stabilizes Cdt2.
(A) 293T cells transfected with Flag-Cdt2 and Myc-Tip60 plasmid in combination with plasmids expressing low risk myc-E6s (From HPV 6, 11, 42) or plasmids expressing high risk myc-E6s (HPV 16,18, 31) were immunoblotted. (B) 293T cells transfected with indicated plasmids were immunoprecipitated with anti-His antibody and immunoblotted (top), or the 10% input cell lysates were immunoblotted (bottom). (C) Confocal immunofluorescence images of HeLa or 293T cells transfected with myc-USP46 plasmid and stained with anti-myc antibody, and DAPI (for nuclei). (D-E) Immunofluorescence images with antibodies indicated on top of 293T cells transfected with His-USP46 plasmid along with myc-E6 plasmids indicated on left. Scale bar indicates 10μm. Quantitation in Fig. S1c. (F) 293T cells transfected with Flag-Cdt2 and indicated E6 variants were immunoblotted as indicated. Table summarizes types of E6 mutations studied and there effect on Cdt2 stabilization with respect to their known p53 degradation activity. (G) 293T cells transfected with variants of E6, Flag-Cdt2 and myc-USP46 were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibody and immunoblotted (top) or 10% input cell lysates directly immunoblotted (bottom). (H) Bacterially expressed GST, GST-16E6F2V+P5R or GST-16E6Y79N (as positive control) bound to glutathione agarose in columns were loaded with purified His-USP46 (lanes 1, 3, 5). Nickel-NTA beads coated with nothing or with HisUSP46 (lanes 2, 4) in columns were loaded with GST-16E6F2VP5R. Bound proteins were eluted and immunoblotted.