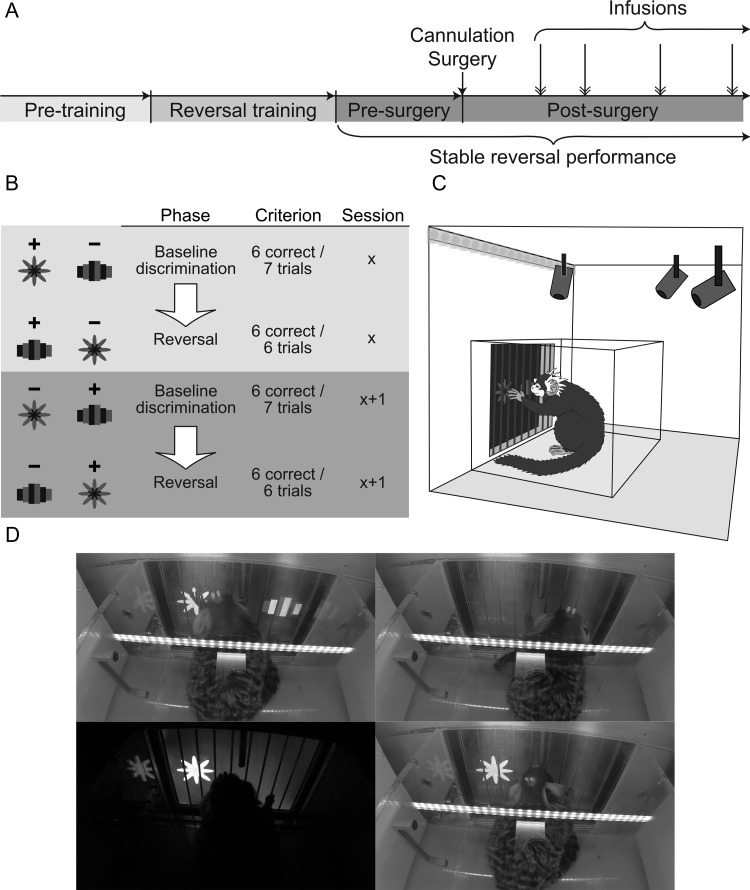
Figure 1.
Schematic of task and experimental design. A. Timeline of experimental protocol. Naïve marmosets were taught to respond on the touchscreen “Pre-training”, and then to perform the serial reversal learning task “Reversal training”. Once marmosets were exhibiting stable reversal performance they underwent cannulation of the medial caudate and anterior putamen. Post-surgery, marmosets received intra-striatal infusions of the GABAA agonist muscimol or saline control infusions on test days. B. Schema illustrating stimulus-outcome contingencies across two consecutive days. After reaching a behavioral criterion of six correct responses within seven trials in the baseline discrimination phase of a session, the stimulus-outcome contingencies were reversed, and the marmoset then had to achieve six correct responses within six trials to pass the reversal phase of the session. The next day, the stimulus-outcome contingency of the baseline discrimination phase was the same as that in the reversal phase of the previous day. C. Diagram illustrating the position of the marmosets within the behavioral testing apparatus and carrying box in relation to the touchscreen, houselights and video cameras. D. Photographs of a marmoset performing the serial reversal learning task, showing counter-clockwise from top left: the marmoset touching a stimulus, punishment darkness following an incorrect response, collection of banana-flavored milk reward following a correct response and an inter-trial interval.