Figure 1.
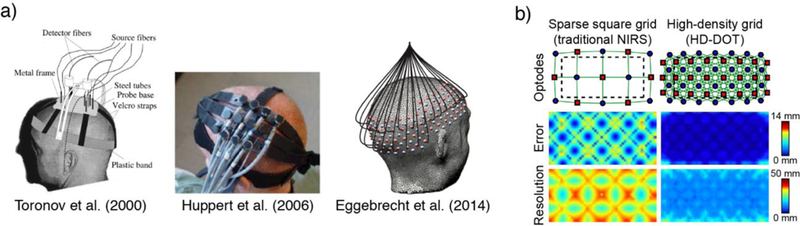
(a) Examples of source and detector arrangements used by Toronov et al. (2000), Huppert et al. (2006), and Eggebrecht et al. (2014). (b) Effects of source and detector spacing on homogeneity of error and effective spatial resolution based on simulated data. Top: source and detector spacing for two example grids. Middle: Localization error, defined as the separation between the known target location and the centroid of the voxels reconstructed above half-maximum contrast. Bottom: Effective spatial resolution, defined as the diameter of the circle centered at each target position needed to enclose the response. Modified from White and Culver (2010).
