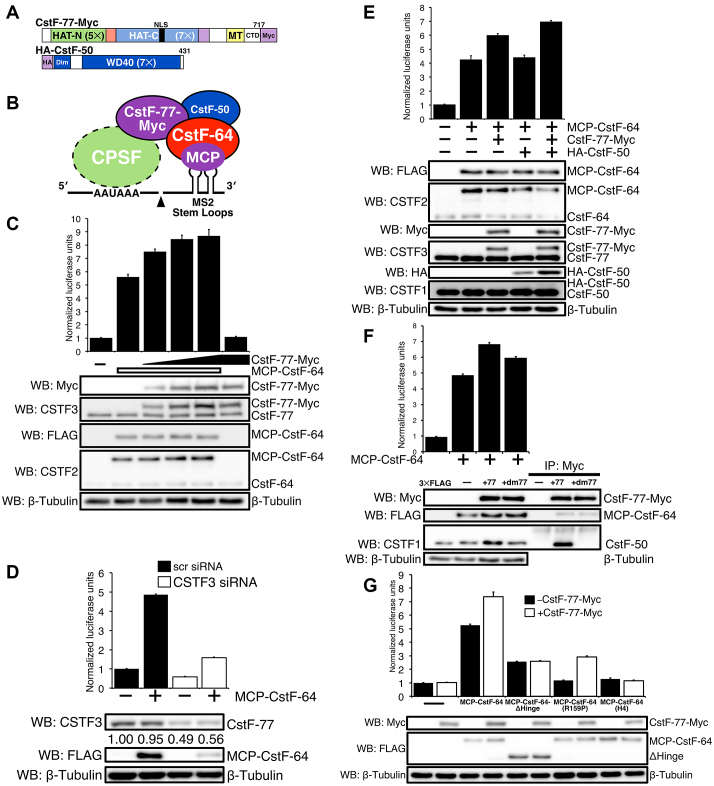
Figure 2.
CstF-77 and CstF-50 enhance MCP-CstF-64-dependent cleavage and polyadenylation. (A) Schematic representation of CstF-77-Myc (CstF-77 with three Myc tags at its carboxy-terminal end) and HA-CstF-50 (CstF-50 with three hemagglutinin tags at its amino-terminal end). The position of the nuclear localization sequence (NLS), position and the number of the carboxy- and amino-terminal HATs, MT and the CTD of CstF-77 are shown. Similarly, the seven WD40 (WD40) repeats and the dimerization (Dim) domains are shown for CstF-50. (B) Cartoon of the interactions between MCP-CstF-64, CstF-77, CstF-50 and SL-Luc reporter construct. (C) Increased amounts of CstF-77-Myc increase C/P as measured by SLAP. Western blots with an antibody against Myc (WB: Myc), against CstF-77 (WB: CSTF3), against MCP-CstF-64 (WB: FLAG) or CstF-64 (WB: CSTF2) are shown. Antibodies against β-tubulin were used as a loading control. (D) Decreased CstF-77 reduces C/P as measured by SLAP. Hela cells were transfected with either a non-specific (scr) or CSTF3-specific siRNAs. Twelve hours after siRNA transfection, cells were transfected for SLAP. Western blots show the reduced expression of the endogenous CstF-77, MCP-CstF-64 (WB: FLAG). (E) HA-CstF-50 co-expressed with MCP-CstF-64 and CstF-77-Myc increases C/P as measured by SLAP. Western blots with the respective antibodies to verify expression of the exogenous proteins through their tags (WB: FLAG, Myc, HA) and antibodies to show relative expression to the endogenous proteins (WB: CSTF1, CSTF2, CSTF3). (F) Mutations in CstF-77-Myc that disrupt the interaction of CstF-77 with CstF-50 reduce C/P as measured by SLAP. Two-point mutations were made in CstF-77 (P584A, M589A, collectively called +dm77) that disrupt the interaction of CstF-77 with CstF-50. Immunoprecipitation with an antibody against Myc tag: no CstF-77, CstF-77-Myc (+77) and CstF-77-Myc-dm77 (+dm77). Western blots for Myc tag (WB: Myc), and endogenous CstF-50 (WB: CSTF1) and β-tubulin were presented. (G) Mutations in MCP-CstF-64 that disrupt the interaction of CstF-64 with CstF-77 decrease both SLAP and the stimulatory effect of CstF-77. MCP-CstF-64-ΔHinge lacks amino acids 96–216 from CstF-64. MCP-CstF-64 (R159P) is a point mutation in the Hinge domain that interrupts the interaction with CstF-77, MCP-CstF-64 (H4) is a series of point mutations in the fourth α-helix of the Hinge domain that interrupt interaction with CstF-77.