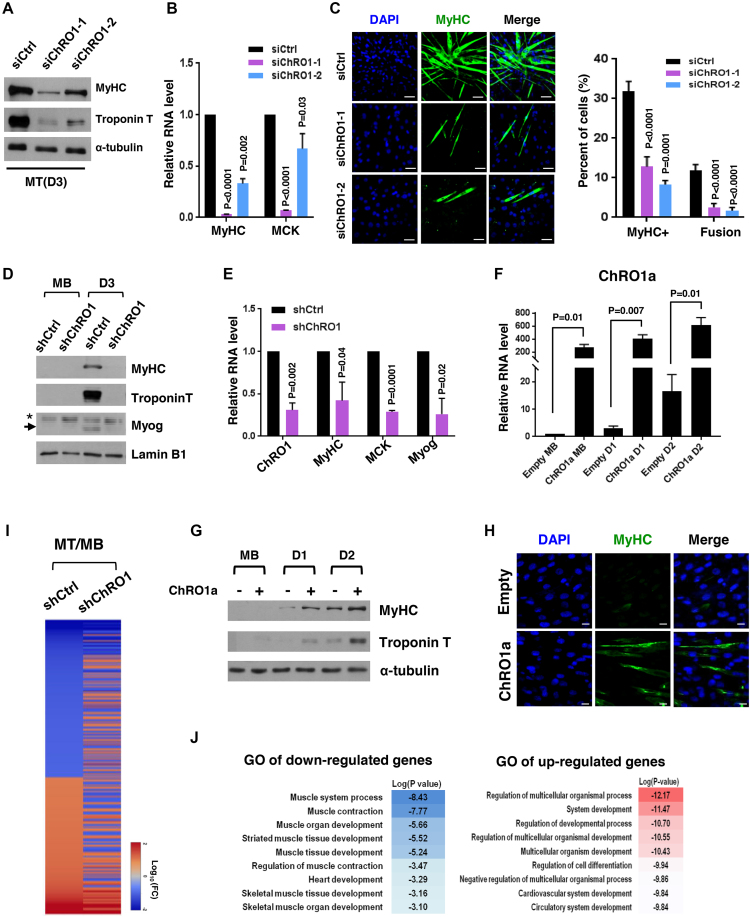
Figure 3.
Muscle differentiation is impaired by ChRO1 depletion. (A) Western blot for MyHC and Troponin T in 3-day differentiated MT after siRNA treatment. α-tubulin was used as a loading control. (B) RT-qPCR for MyHC and muscle creatin kinase (MCK) in siRNA-treated C2C12 that was differentiated for 3 days. (C) Representative immunofluorescence for MyHC and DAPI staining. Scale bars, 50 μm (left). MyHC-positive cells and fusion index in MT (right). (D) Western blots for MyHC, Troponin T and Myogenin in either shCtrl or shChRO1 MB and MT (Day 3). Lamin B1 was used as a loading control. *: non-specific band, arrow indicates Myogenin. (E) RT-qPCR for ChRO1, MyHC, MCK and Myogenin in shCtrl or shChRO1 MT (Day 3). (F) RT-qPCR of ChRO1a in empty or ChRO1a over-expressing C2C12 cells in growing (MB) or differentiation (Day 1, Day 2) medium. n = 4 independent experiments. (G) Western blots for MyHC and Troponin T with ChRO1a over-expressing MB and MT (Day 1, Day 2). α-tubulin was used as a loading control. (H) MyHC immunostaining of 1 day-differentiated C2C12 cells over-expressing ChRO1a. Scale bars, 50μm. (I) Differentially expressed genes of shCtrl or shChRO1 C2C12 (Fold Change > 2, P < 0.05). Data are shown as log 10 of fold change. (J) Gene ontology analysis of ChRO1-depleted cells, shown in log P-value.