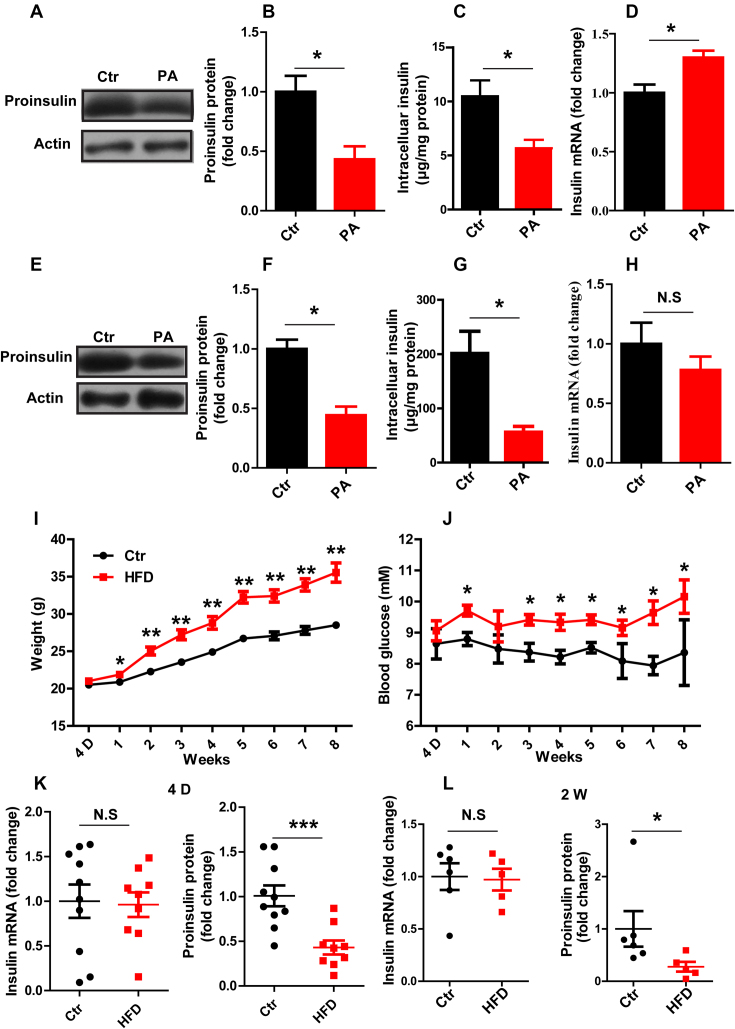
Figure 1.
Insulin translation is inhibited in vitro and in vivo after FFA treatment. (A, E) Western blotting was used to determine proinsulin expression. (B, F) The fold change in proinsulin expression was determined by normalization to actin expression. (C, G) ELISA was used to detect the intracellular insulin content. (D, H) RT-qPCR was used to determine the insulin mRNA level in Control (Ctr) and PA-treated (PA) INS-1 cells (A–D) and in mouse islets (E–H) in vitro (n ≥ 3). The weight (I) and random blood glucose levels (J) in control (Ctr) and high-fat diet (HFD) mice were monitored for 8 weeks (n = 15/15). RT-qPCR was used to determine the insulin mRNA level, and western blotting was used to determine proinsulin protein expression at different time points, namely, 4 days (K) and 2 weeks (L). The results are shown as the means ± SEMs. Significance was determined by a two-tailed unpaired t-test; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; N.S, no significance.