Figure 1.
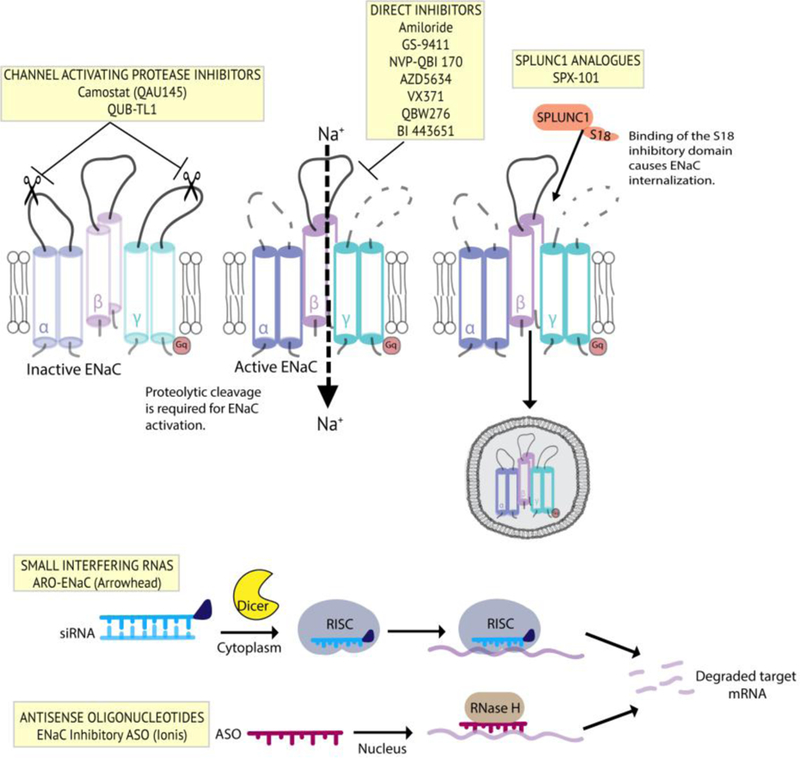
Summary of ENaC inhibitor therapies for CF. Clockwise from top left: channel activating protease inhibitors which prevent proteolytic cleavage of the extracellular loops of a- and g-ENaC; direct inhibitors which decrease channel open probability through direct interaction with the channel; peptide analogues which mimic the regulatory effects of the SPLUNC1 secreted protein; antisense oligonucleotide therapies which degrade ENaC mRNA transcripts through the RNase H mechanism; siRNA therapies which degrate ENaC mRNA transcripts though the RISC mechanism.
